Twenty years ago this week, the United States government placed Haiti’s elected president, Jean-Bertrand Aristide, on a plane sent from Guantanamo Bay and headed for the Central African Republic with a false flight plan. The flight consummated a coup d’état that ended a decade of hard-won democratic progress.
It also began two decades of dismantling of democracy by U.S.-backed Haitian regimes. Haiti is “celebrating” the coup anniversary without a single elected official in office and no elections in sight, while most Haitians face catastrophic humanitarian conditions.
The U.S. government officially denies a coup took place and claims it did not force Aristide to flee. But the February 29, 2004 coup d’état successfully removed a regional leader who resisted complying with U.S. prescriptions. The following 20 years of supporting governments opposed to Aristide — most of them unelected or elected in flawed elections— have prevented the emergence of other non-compliant Haitian leaders.
But as the United States faces its own election this year that President Biden calls an existential threat to our democracy, and struggles with the arrival of Haitians fleeing the horrific conditions that our policies helped generate, it is time to reconsider this approach.
The United States actually restored Aristide before it toppled him. In 1994, President Clinton launched Operation Restore Democracy to return Aristide from his exile caused by a 1991 military coup. Aristide left office at the end of his term in 1996, in the first-ever transfer of power from one elected Haitian president to another. He returned to the presidential palace in Haiti’s second democratic transfer of presidential power, in 2001.
But U.S. leaders did not like the direction Haiti’s restored democracy took. They particularly resented President Aristide challenging the United States by trying to raise the minimum wage for workers sewing Americans’ clothes, defying “small government” dogma by increasing government investment in education and healthcare, speaking out against the unjust international order, and demanding $21 billion from France as restitution of the “independence debt” that France extorted in 1825.
These policies were immensely popular in the areas of Haiti that lay outside the U.S. Embassy compound. In 2000, Haitians voted overwhelmingly for Aristide and his Lavalas party. But the United States used a minor controversy over alleged technical election irregularities as a pretext to impose a development assistance embargo that brought Haiti’s economy and its government to its knees. An insurgency led by former soldiers attacked the weakened government from across the border in the Dominican Republic, setting the stage for the U.S. to force Aristide into exile.
Haiti has never recovered the level of democracy it had before Aristide’s departure. The past 20 years have seen just a single transfer of power from one elected president to another, in 2011. For over half that time, Haiti’s parliament has been unable to hold votes, because the failure to run elections left it with too few members. For a quarter of that time there has been no elected president in office.
Haiti’s last elections were in 2016, and parliament has not held votes since 2019. There has been no president since July 2021, when then-President Jovenel Moise, who had stayed in office five months past the end of his term, was assassinated. Haiti is led by a de facto prime minister, Ariel Henry, who was chosen not by Haitians but by the Core Group, a group of mostly majority-white countries led by the United States. Henry’s reign is unconstitutional and faces widespread Haitian opposition. But with the United States propping him up, Henry has been able to serve a longer term than any prime minister in at least 40 years.
That persistent support has both seriously weakened promising civil society mobilization toward a broad-based democratic transitional government and removed any incentive for Henry to make meaningful compromise towards fair elections that he and his party cannot win. The U.S. responded to Henry’s intransigence by leading the creation of the foreign armed intervention he requested that Haitians say will only further entrench Henry’s rule.
Meanwhile Haitians face intolerable conditions. Gangs control much of the country, including an estimated 80% of the capital, Port-au-Prince. The economy has had both zero growth and inflation over 15% for three years straight. Children face unprecedented levels of wasting hunger. To spare themselves and their families from this nightmare, hundreds of thousands of Haitians have made the desperate voyage out of Haiti, often arriving at the U.S. border.
President Biden’s concerns about U.S. democracy should inform his approach to Haiti. His defense of democracy as “America’s sacred cause” is weakened when his own administration persistently maintains an illegal Haitian government in power precisely because it will obey the dictates of U.S. presidents over the priorities of Haitian voters. If President Biden is serious about democracy, he would allow Haitian voters the opportunity to choose their leaders.
- Supporting Moïse, Washington lost Haitian trust ›
- The int'l community must resist calls for 'muscular intervention' in Haiti ›
- US should let Haiti reclaim its democracy | Responsible Statecraft ›
- US ‘prepared’ to deploy troops to Haiti if necessary | Responsible Statecraft ›
- US-backed, Kenya-manned police mission in Haiti is struggling | Responsible Statecraft ›
- Further US intervention in Haiti would be worst Trump move of all | Responsible Statecraft ›

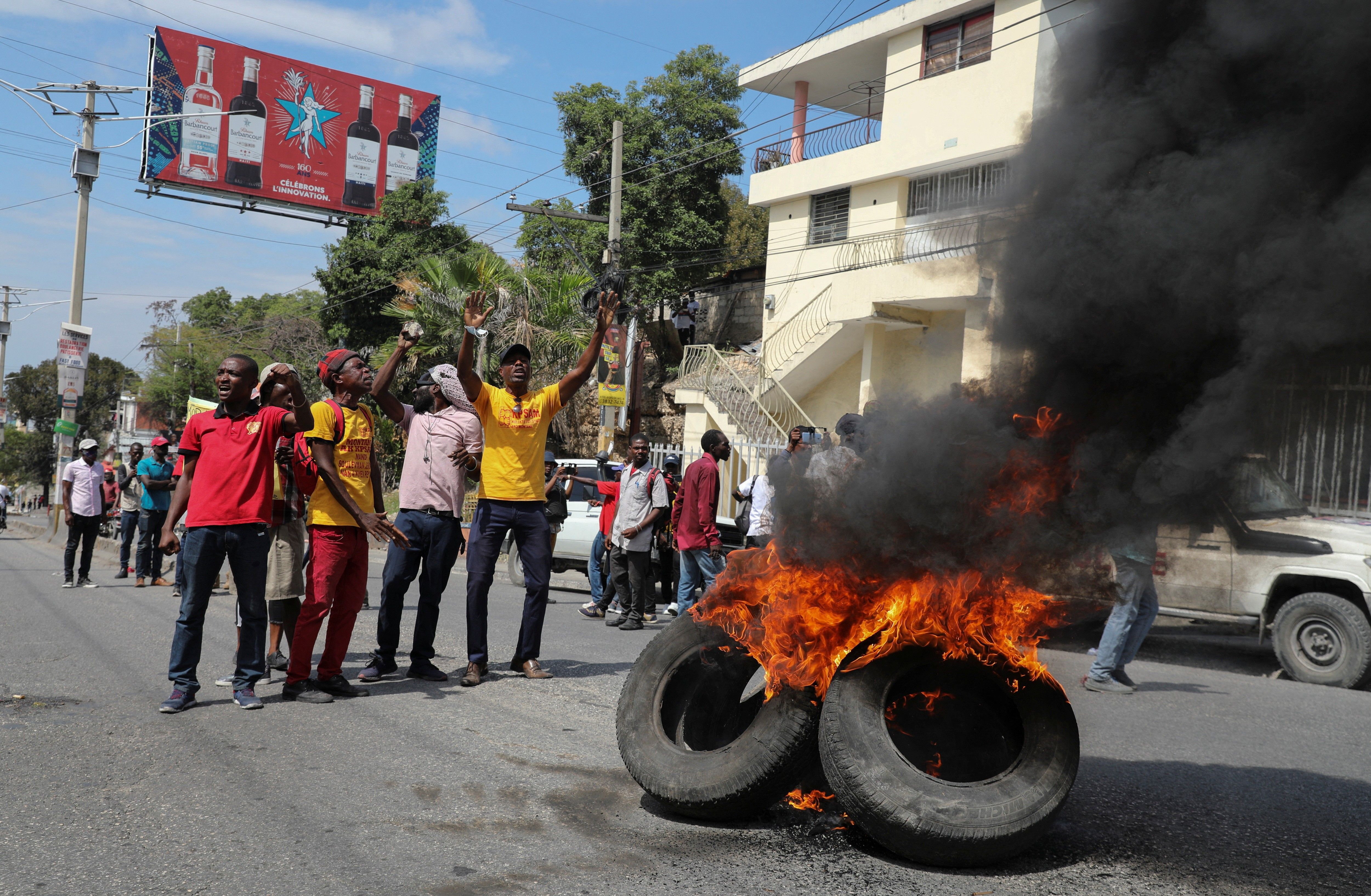


 Screengrab via niacouncil.org
Screengrab via niacouncil.org Screengrab via niacouncil.org
Screengrab via niacouncil.org











