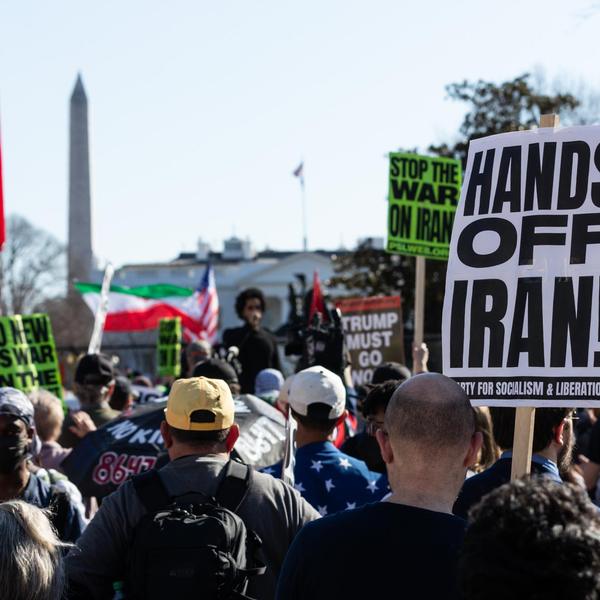
The Senate largely along partisan lines voted down a resolution that would have prevented President Trump from launching further attacks on Iran.
The resolution — introduced by Sen. Tim Kaine (D-Va.) just days before U.S. military forces bombed Iranian nuclear sites last Saturday — failed by a vote of 47-53, with Sen. John Fetterman (D-Pa.) breaking ranks with Democrats in voting against, and Sen. Rand Paul (R-Ky.) the only Republican supporting.
It’s unclear what those strikes accomplished. While President Trump has been boasting about their alleged impact, saying they “obliterated” Iran’s nuclear program, a leaked assessment from the Defense Intelligence Agency found that they “did not,” as CNN first reported, “destroy the core components of the country’s nuclear program and likely only set it back by months.”
Meanwhile, Rafael Grossi, head of the International Atomic Energy Agency said on Friday that Iran’s nuclear facilities “suffered enormous damage” from the U.S. attack. A CIA assessment headed by Director John Ratcliffe a day after the DIA leak said "new intelligence from a historically reliable source/method that several key Iranian nuclear facilities were destroyed and would have to be rebuilt over the course of years.” Senators briefed behind closed doors Thursday came away with different impressions of the damage.
Hours before the vote, Kaine noted that the framers of the U.S. Constitution “decided that war was too big a decision for one person” and said “the United States should not be at war without a vote of Congress.”
Later in his remarks, the Virginia Democrat highlighted one of Trump’s recent social media posts in which the president shared a parody of the Beach Boys’ song “Barbara Ann” that was about bombing Iran. Kaine then recalled the framers’ stance on war powers: “We shouldn't premise a decision to send our sons and daughters into war on the judgment of a single person.”
Sen. Todd Young (R-Ind.) — who has previously championed Congress’s war powers role over the executive branch — opposed Kaine’s resolution, saying before the vote that he was “confident that Iran was prepared to pose a significant threat to the security of the United States and Israel, making the president’s decision to pursue limited, targeted action necessary and based on the appropriate legal foundation.” He said he thinks Kaine's resolution is unnecessary because Trump got a ceasefire and is purportedly not seeking more military action.
Sen. Mike Lee (R-Utah), who also previously supported efforts at reining in the executive branch's war powers, voted against the Kaine-sponsored measure on Iran.
Sen. Paul, who supported the resolution, said just before the vote that he was doing so “to stand up for the Constitution, to stand up for American service members and to stand up for America's strategic interest.”
Paul chastised those clamoring for more war with Iran.
“Many advocates for war, giving voice to their real feelings, have loudly opposed the current cease fire,” he said. “Those arguing against a cease fire give a callous testimony, insensitive to the cruelties of war.”
Paul added, “The American people are sick and tired of sending their children to fight and die in war zones on the other side of the world with no tangible U.S. interests at stake, abdicating our constitutional responsibility by allowing the executive branch to unilaterally introduce U.S. troops into wars is an affront to the Constitution and to the American people.”
The House will vote on similar war powers-related legislation in the coming weeks, one of which is bipartisan, led by Reps. Ro Khanna (D-Calif.) and Thomas Massie (R-Ky.).
- Congress moves to put the brakes on Trump's unilateral bombing ›
- Poll: Trump voters don't want US involved in Israel’s war on Iran ›
- If Iranian regime collapses or is toppled, 'what's next?' ›
- Senate blocks effort to rein in Trump's war on 'narco-terrorists' | Responsible Statecraft ›
- On war, has my party become 'eunuchs in the thrall' of Trump? | Responsible Statecraft ›