Israel’s war on Gaza has significantly internationalized with its expansion into the Red Sea since November. This body of water, which is critical from the standpoint of global trade, is consequently becoming increasingly militarized.
Members of NATO have been divided in their responses to the Red Sea security crisis. Some states in the Transatlantic alliance have favored a more militaristic approach to dealing with Houthi missile and drone attacks against commercial and merchant vessels. But others have warned that such action only risks escalating tensions.
Beginning on January 12, the U.S. and UK — with nonoperational support from Australia, Bahrain, Canada, and the Netherlands — began bombing dozens of Houthi targets in various parts of Yemen. Additional rounds of bombing followed, and Washington and London are continuing these strikes against Ansarallah. However, France, Italy, and Spain have notably refused to take part in those U.S.-led military operations while instead opting for a more diplomatic approach to the Red Sea security crisis.
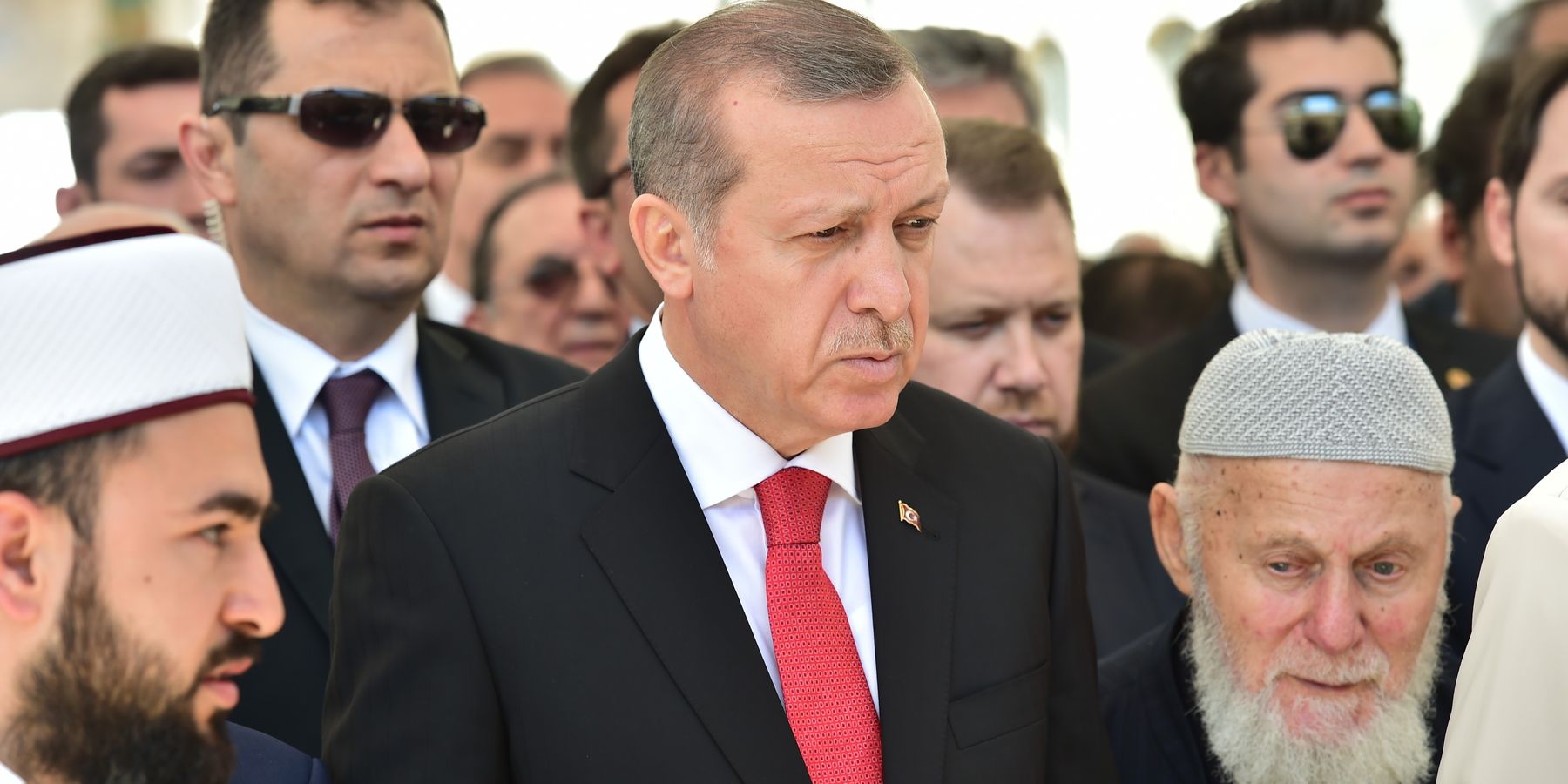
Turkey says ‘no’ to bombing the Houthis
The NATO member most staunchly opposed to such Western military intervention against Ansarallah is Turkey. President Recep Tayyip Erdogan went as far as accusing Washington and London of “trying to turn the Red Sea into a sea of blood.”
Erdogan’s remark should be at least partly understood within the context of Turkish domestic politics at a time in which much of the general public is angry about Israel’s industrial slaughter in Gaza. Particularly in the Turkish social media sphere there is a “rising tendency to glorify the Houthi war against Israel,” said Betul Dogan-Akkas, an assistant professor of international relations at Ankara University, in an interview with RS. She explained that there is a general lack of knowledge among the general Turkish public about the Houthis but also a shared belief that state and non-state actors should support Gaza, which many Turks perceive the Houthis to be doing.
Dogan-Akkas added that Erdogan has been keen to criticize some of Turkey’s traditional Western allies for not taking any action against Israel in response to its behavior in Gaza since October while using, what Ankara sees as, disproportionate force against the Houthis in response to their maritime attacks.
Although Erdogan’s statements are frequently intended for domestic consumption, Turkey’s president and high-ranking officials in Ankara seem gravely concerned about U.S.-UK military action in the Red Sea worsening regional tensions that could risk bringing NATO into a much larger conflict.
“It is not [in] Ankara’s interests for the crisis to escalate, and Turkey would not benefit from a collective effort to attack Houthi targets given Erdoğan’s desire to remain equidistant from the sides of the conflict,” Batu Coşkun, a political analyst who specializes in Turkish affairs at the Sadeq Institute, told RS. “These concerns are likely being brought up by Turkish officials in NATO meetings as well.”
“Turkey is not directly party to the growing hostilities in the Red Sea and has in essence adopted a position of active neutrality. The government was even quick to downplay an incident where Houthi linked pirates boarded and detained a Turkey bound vessel,” he added.
Turkey, as a maritime power with vested interests in Africa and the Arabian Peninsula, has high stakes in the outcome of the Red Sea security crisis and militarization. Turkey’s economy has been paying a price for increased freight costs with large container ships rerouting to avoid the Red Sea altogether because the Houthi maritime attacks.
Trade between Turkey and Far East countries such as China, which is Turkey’s number one supplier of goods, must now go around South Africa and through the Strait of Gibraltar instead of through the Bab al-Mandab. Also, India, Malaysia, and South Korea make the list of Turkey’s top 20 import partners.
Enter Somalia
Last month, Turkey and Somalia signed the Framework Agreement for Defence and Economic Cooperation, which is a 10-year pact that purportedly involves Ankara in developing, training, and equipping the Somali naval forces while establishing Turkey as the protector of Somalia’s coastline and ultimate maritime security guarantor. Building on that agreement, Turkey and Somalia signed an inter-governmental energy cooperation deal on March 7, which will further boost bilateral relations and increase Turkey’s role in the Horn of Africa.
Ankara and Mogadishu’s defense and economic cooperation will reach new heights with Ankara having “expansive and unlimited” control in Somalia, according to one Mogadishu-based analyst. From a regional standpoint, Turkey is set to step up its activities as an increasingly influential actor in the Gulf of Aden’s security landscape, which, as Coşkun explained, means that “Turkish maritime assets will now be present in proximity to the escalating crisis in the Red Sea.”
As Red Sea security continues to suffer from the Gaza war’s expansion, Ankara will probably continue pursuing policies aimed at sparing Turkey from becoming excessively entangled. Ankara’s participation in Western-led initiatives aimed at “deterring” Ansarallah from more missile and drone strikes against ships is highly unlikely. Rather than aligning with Washington and London against the Houthis, Turkey will attempt to balance itself between the various actors in Yemen and the Red Sea while also positioning Ankara as a defender of the Palestinians in Gaza.
“Amid insecurity in the Red Sea, Ankara benefits from being an actor that all parties are seeking to engage with. Turkey remains tethered to the Transatlantic alliance by virtue of a unified security architecture. However, [Turkey] sits at a somewhat unique position where its regional relations remain equally significant,” Coşkun told RS.
- Houthi attacks underscore failures of Biden Red Sea strategy ›
- Red Sea is today's arena for clash of African-Arab power politics ›
- The cost of US fighting Houthis in the Red Sea just went up ›
- Erdogan v. Netanyahu: where does this go? | Responsible Statecraft ›
- Will Turkey eventually support Hezbollah? | Responsible Statecraft ›