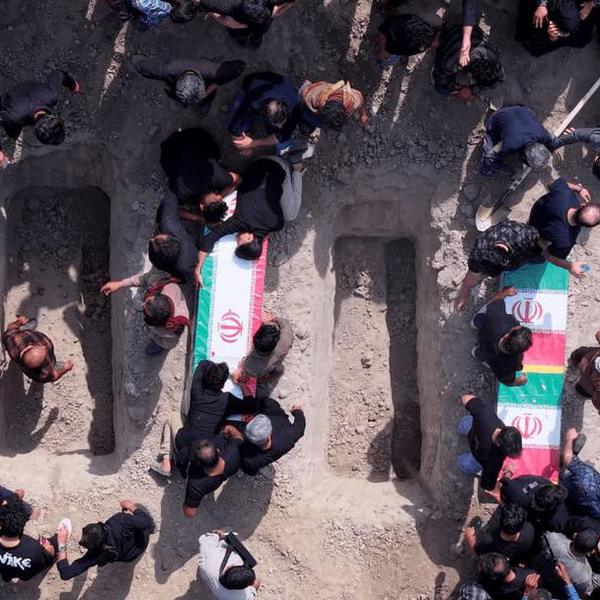
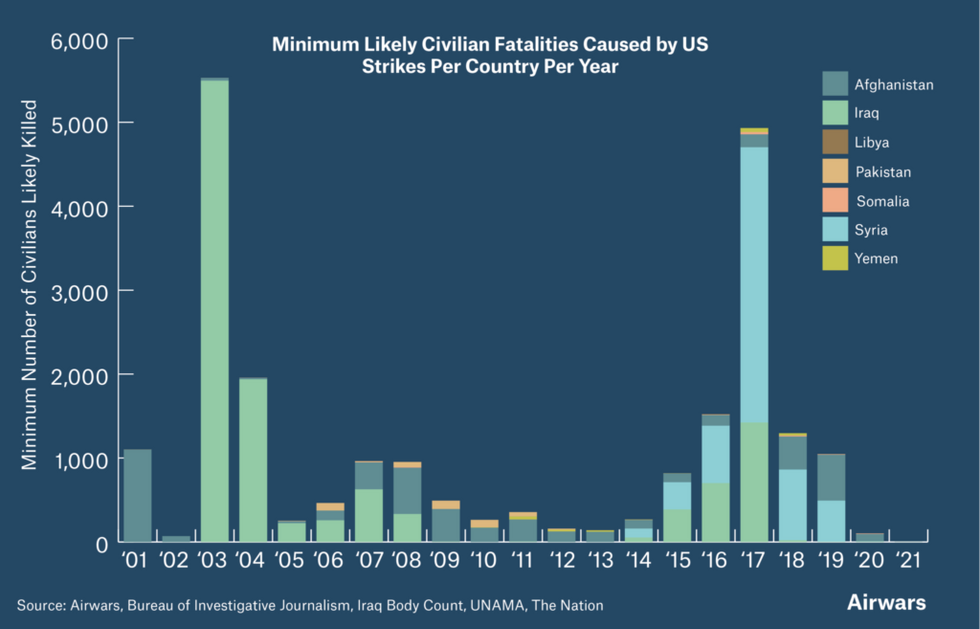
A new study released on Monday found that U.S. airstrikes during the two-decade-long post-9/11 wars have killed at least 22,679 civilians in seven countries throughout the greater Middle East.
According to Airwars, which tracks civilian casualties in conflict zones, the United States declared that it had conducted at least 91,340 strikes in those seven countries — Afghanistan, Iraq, Libya, Pakistan, Somalia, Syria, and Yemen — and that as many as 48,308 civilians were killed as a result.
Airwars explains the difference in estimates as follows: "The gap between these two figures reflects the many unknowns when it comes to civilian harm in war. Belligerents rarely track the effects of their own actions – and even then do so poorly. It is left to local communities, civil society and international agencies to count the costs. Multiple sources can however suggest different numbers of fatalities, meaning that monitoring organisations like Airwars will record both minimum and maximum estimates."
The group also says that it “has examined only direct harm from U.S. strikes since 9/11 — with many of our sources providing conservative casualty estimates. We are therefore looking at a fraction of the overall civilian harm in these countries.”
The Airwars estimate comes on the heels of a new report from Brown University’s Costs of War Project which found that between 897,000 and 929,000 had been “directly killed” in the post-9/11 wars, and that around 365,000 of those were civilians. The Project estimated that total costs so far at nearly $8,000,000,000,000.
“As part of our research,” Airwars says, “we also sought official U.S. military estimates for the numbers of civilians killed by its own actions since 9/11. Neither CENTCOM nor the Department of Defense have published such findings.”