A video on Congress.gov, overlayed with an uplifting guitar melody, explains what committee hearings are supposed to do; A hearing “provides a forum at which committee members and the public can hear about the strengths and weaknesses of a proposal from selected parties,” the disembodied voice says.
If only it were that simple.
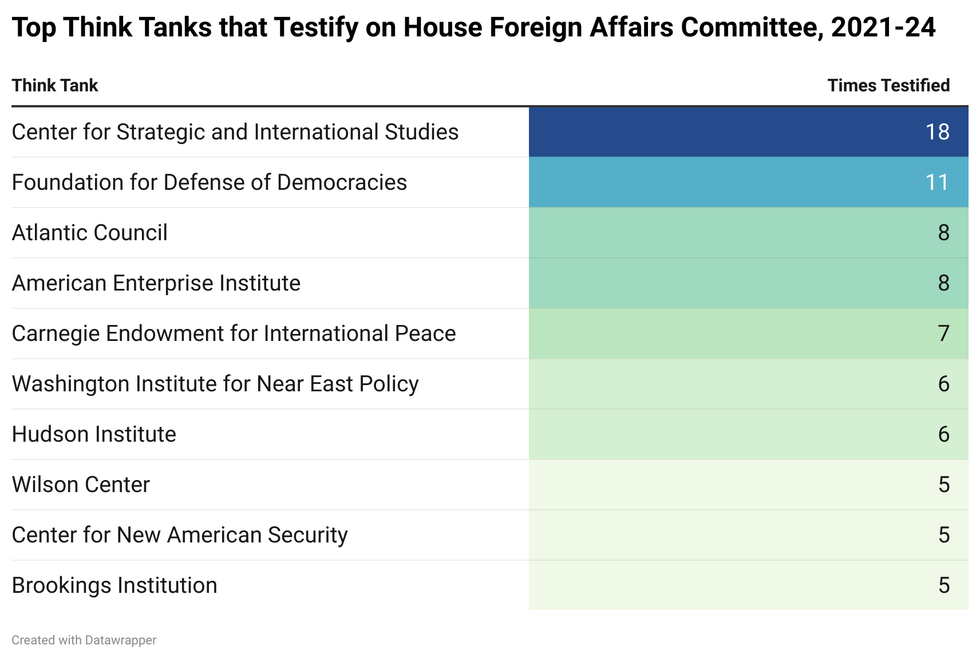
In practice, hearings often give experts whose employers are funded by special interests a platform to publicly lobby Congress. From 2021 to 2024, 378 non-governmental witnesses testified before the House Foreign Affairs Committee, the House body that oversees foreign assistance, war powers, and arms exports, among other key foreign policy-making decisions. Just over one third of those witnesses — 137 of them — came from the world of think tanks.
A Responsible Statecraft analysis of think tank annual reports and congressional witness lists shows that a majority of the think tanks represented on the witness list cash checks from weapons manufacturers and foreign governments. Eighty-nine percent of think tank affiliated witnesses work for organizations that accept foreign government funding. The number is only slightly lower for the arms industry; 79% of witnesses affiliated with think tanks represent organizations that take donations from the top 100 Pentagon contractors.
In fact, less than 7% of think tank witnesses are affiliated with organizations that publish a list of their donors and say they do not accept funding from both Pentagon contractors and foreign governments. In other words, think tanks with Pentagon contractor or foreign government funding are called to testify nearly 14 times as often as think tanks without these financial ties.
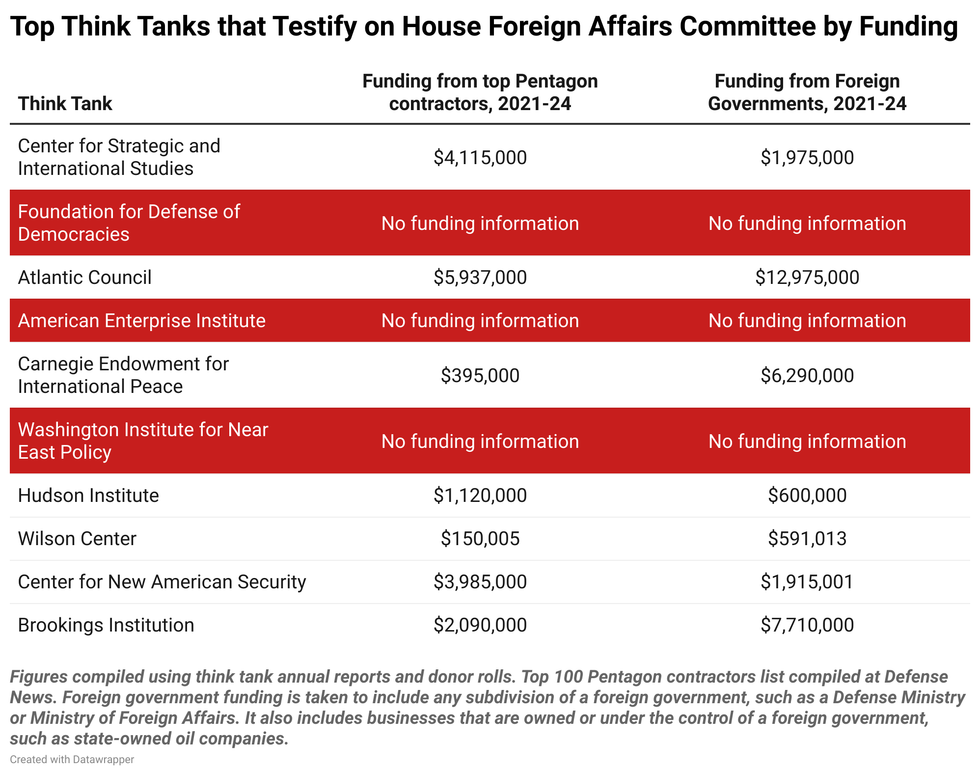
And, the money flowing from Pentagon contractors and foreign governments to these think tanks hasn’t been trivial. As documented in a forthcoming Quincy Institute brief on think tank funding, between 2021 and 2024, think tanks that were represented on the witness stand received at least $20 million dollars from the top 100 Pentagon contractors and $64 million from foreign governments. Though, the real number is likely much, much, higher, given the murky world of dark money think tanks, anonymous donors, and misleading funding ranges.
Non-governmental congressional witnesses have to fill out a conflict of interest disclosure known as a “Truth in Testimony” form. The form asks witnesses to disclose funding from foreign governments and federal grants related to the hearing subject. Yet, many witnesses exploit a loophole that allows them to avoid disclosure if they declare they are simply testifying on their own behalf, even if they do just happen to work for an organization that receives considerable funding from special interests that could benefit from the witnesses’ recommendations. And, because there is a lack of enforcement, witnesses often simply leave these forms blank.
In the House Armed Services Committee — the committee that oversees defense policy and the annual defense budget — the numbers were even more stark, albeit with a much smaller sample size. All but one of the 19 think tank witnesses appeared in front of the HASC on behalf of an organization that accepts Pentagon contractor funding.
While all of this funding could lead to conflicts of interest at the witness stand, lawmakers and the public can at least follow the paper trail by looking at think tank annual reports. However, because there is no legal requirement for think tanks to disclose their donors, there are a host of witnesses that testify on national security that hail from “dark money” think tanks — think tanks that disclose no information about their funding sources.
Eli Clifton, Senior Adviser and Investigative Journalist at the Quincy Institute, explained in an interview with RS that it can be difficult to know when some witnesses have a potential conflict of interest given the preponderance of dark money think tanks. Clifton previously documented how dark money think tanks dominate the witness table at House Foreign Affairs Committee hearings. In his investigation from 2017-2020, he found that only “30 percent of think tank affiliated witnesses appeared on behalf of institutions that fully disclose their donors.”
Between 2021 and 2024, this figure remains largely unchanged as only 34% of think tank witnesses came from organizations that fully disclose their donors. Another third of witnesses hail from dark money think tanks, and the last third are affiliated with think tanks that are only partially transparent. Some of the top testifiers, such as the Foundation for Defense of Democracies, the American Enterprise Institute, and the Washington Institute for Near East Policy — all think tanks that often promote a more militaristic U.S. foreign policy — do not disclose any information about donors.
“The idea that dark money think tanks are regularly testifying before Congress while providing no details about their funding is concerning. It undermines trust in think tanks and in experts,” said Clifton.
An emerging body of scholarship indicates that think tank funding influences behavior and research products. Daniel Schuman, executive director of the American Governance Institute, explained in an interview with RS that “it’s basic human psychology that donors' generosity is often connected to people espousing certain viewpoints.”
A 2014 New York Times exposé on foreign government funding of think tanks cited congressional testimony as evidence that “[t]he line between scholarly research and lobbying can sometimes be hard to discern.”
If an expert testifies against the interests of major donors, they run the risk of having to find a new donor — or in some cases, a new job. The Times investigation also detailed an episode with Michele Dunne, then Director of the Atlantic Council’s Rafik Hariri Center for the Middle East. Dunne broke with the Center’s funder, Bahaa Hariri, when she testified in front of the Senate Foreign Relations Committee that the U.S. should suspend military aid to Egypt in 2013 in response to a coup led by Abdel Fatah el-Sisi. Hariri called the Atlantic Council to complain and within four months, Dunne was out of a job. Fred Kempe, the president of the Atlantic Council, said at the time that differences Dunne may have had with colleagues and donors were inevitable and “don’t touch our fierce defense of individual experts’ intellectual independence.”
Less attention has been paid to Pentagon contractor-funded think tank experts on the witness stand.
“About half of the defense budget lands on the gravy train to Pentagon contractors, which then use some of that money to fund researchers, academics, and think tank experts,” Schuman said. “Some of those scholars may then distance themselves from the funding by testifying in their personal capacity, but oftentimes their conclusions are indistinguishable from the interests of their donors.”
At a September 19 hearing on Iran, for example, three witnesses who testified were affiliated with think tanks — the Center for a New American Security, the Atlantic Council, and the Council on Foreign Relations — that received funding from Pentagon contractor donors that could rake in profits from a military-first approach to Iran.
One witness, Kirsten Fontenrose, even argued that the U.S. should pass an Authorization for the Use of Military Force. “The U.S. should make it clear to the leadership of Iran’s proxy, drone and missile programs that new capabilities now permit the U.S. and partners to dismantle their facilities and chains of command with low to no risk of negative secondary effects," she said. "Though ‘AUMF’ is a four letter word in Congress, an Authorized Use of Military Force could convey this quickly and clearly.”
Fontenrose is also the president of Red Six Solutions, a red team defense consulting company and Pentagon contractor that prepares clients for threats against unmanned aerial systems.
At a separate hearing on Iran in February, American Enterprise Institute Senior Fellow Kenneth Pollack argued that the U.S. should become more involved in Yemen’s civil war in arming, equipping, and training the anti-Houthi coalition.
“It could mean employing American air power as well, as we did in support of Iraqi forces against ISIS in 2014 to 2018,” said Pollack.
AEI does not publicly disclose its donors, but a staffer there let slip at an event last year that it is funded by Pentagon contractors. “We’d be remiss if we didn’t mention that both Lockheed and Northrop provide philanthropic support to AEI. We are grateful for that support,” an AEI moderator announced.
Even with an incomplete picture due to dark money think tanks, it’s clear that Congress is almost exclusively hearing one side of the debate. If congressional hearings are meant to gather information and hear the “strengths and weaknesses” of proposals, lawmakers should look to diversify the witness list. If there is no countervailing voice, the status quo can lead to an entire sector singing in chorus at the witness stand for things that will serve the interests of Pentagon contractors and foreign governments, not the United States.
- New study reveals rampant conflicts of interest at think tanks ›
- Bipartisan 'Fighting Foreign Influence Act' targets think tank funding ›
- DC think tank addresses undisclosed conflicts of interest ›
- Big mouths for weapons spending are mum on industry backers ›
- New poll shows people distrust think tanks even more than media ›
- New report shows more than $1B from war industry and govt. going to top 50 think tanks ›
- New Report Details $174 Million in Foreign Funding to D.C. Think Tanks ›
- Will Defense Policy Board continue to be a refuge for the Blob? | Responsible Statecraft ›




 Screengrab via niacouncil.org
Screengrab via niacouncil.org Screengrab via niacouncil.org
Screengrab via niacouncil.org











