It is possible to actually measure Washington's dishonesty. How big is it? It’s about 600 miles.
In 1990, according to declassified documents, Secretary of State James Baker assured Soviet leader Mikhail Gorbachev that NATO would not expand “one inch” east of Germany. Thirty years ago, that was Russia’s red line.
On December 2, that red line moved from one inch to 600 miles as Vladimir Putin said he would now seek a promise that NATO would not expand further east to Ukraine.
Since these assurances, NATO has wandered its way through Hungary, the Czech Republic, Estonia, Latvia, Lithuania, Bulgaria, Romania, Slovakia, Slovenia, Albania, Croatia, Montenegro and Poland. Six hundred miles of broken pledges have brought the U.S. and NATO to the border of Ukraine.
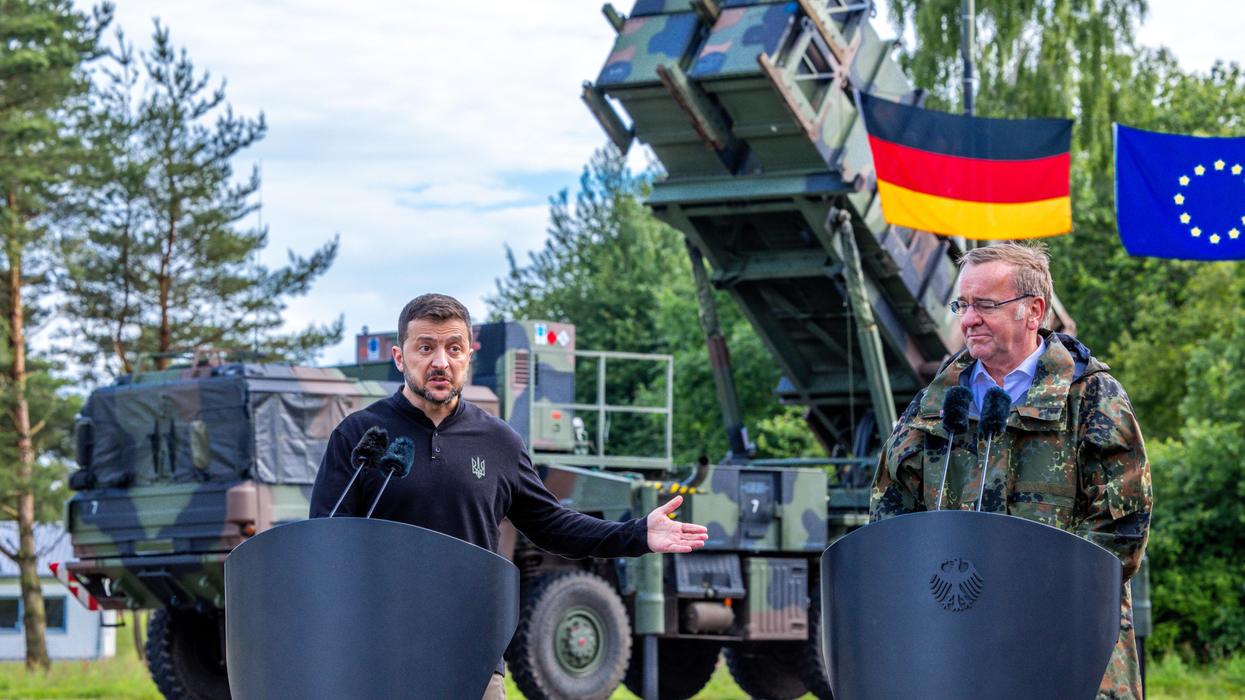
On September 1, President Biden met with Ukrainian President Volodymyr Zelensky at the White House. Biden used code words for NATO encroachment when he pledged his "support for Ukraine’s Euro-Atlantic aspirations" and American support for Ukraine’s "being completely integrated in Europe." He then announced "a new $60 million security assistance package" in addition to the $400 million in security assistance the U.S. has already provided Ukraine this year.
Having retreated 600 miles from Gorbachev’s red line, Putin drew a new red line on December 2, seeking “reliable and long-term security guarantees.” Those guarantees “would exclude any further NATO moves eastward and the deployment of weapons systems that threaten us in close vicinity to Russian territory.”
Putin is keenly aware that the red line has moved east 600 miles. At the Munich Conference on Security Policy in 2007, Putin asked the world, “And what happened to the assurances our Western partners made after the dissolution of the Warsaw Pact? Where are those declarations today? No one even remembers them. But I will allow myself to remind this audience what was said. I would like to quote the speech of NATO General Secretary Mr. Woerner in Brussels on 17 May 1990. He said at the time that: ‘the fact that we are ready not to place a NATO army outside of German territory gives the Soviet Union a firm security guarantee.’ Where are these guarantees?”
The guarantees were a deception, and the red line has moved hundreds of miles and has become a threat. Seven years later, in its review of 2014, Russia’s Ministry of Foreign Affairs would note that the “ongoing eastward expansion [and] successive waves of NATO enlargement [are] contrary to the assurances issued at the highest level.” In 2015, Russia’s National Security Strategy would note that NATO’s “continued expansion and the approach of its military infrastructure to Russia’s borders, all create threat to national security.”
The first guarantee was given on February 9, 1990 when Secretary of State Baker assured Gorbachev that if NATO got Germany and Russia pulled its troops out of East Germany, NATO would not expand east of Germany. Gorbachev records in his memoirs that he agreed to Baker’s terms “with the guarantee that NATO jurisdiction or troops would not extend east of the current line.”
In his book Superpower Illusions, Jack F. Matlock Jr., who was the American ambassador to Russia at the time and was present at the meeting, confirms Gorbachev’s account, saying that it “coincides with my notes of the conversation except that mine indicate that Baker added 'not one inch.'”
The next day, according to West German foreign ministry documents, on February 10, 1990, West German Foreign Minister Hans-Dietrich Genscher told his Soviet counterpart Eduard Shevardnadze “‘For us . . . one thing is certain: NATO will not expand to the east.’ And because the conversation revolved mainly around East Germany, Genscher added explicitly: ‘As far as the non-expansion of NATO is concerned, this also applies in general.’”
Even earlier, on January 31, 1990, Genscher had said in a major speech that there would not be “an expansion of NATO territory to the east, in other words, closer to the borders of the Soviet Union.”
The National Security Archive published the actual documents detailing what Gorbachev was promised on December 12, 2017. According to the late Stephen Cohen in his book, ”War With Russia?” the documents finally, and authoritatively, reveal that, “the truth, and the promises broken, are much more expansive than previously known: all of the Western powers involved — the US, the UK, France, Germany itself — made the same promise to Gorbachev on multiple occasions and in various emphatic ways.”
It didn’t have to be this way. Like Gorbachev before him at the end of the cold war, Putin has hoped to help create an international community that, rather than building blocs, featured cooperation among equals. He had even suggested Russian membership in NATO. Even in the speech where he drew Russia’s new red line, Putin was still suggesting a cooperative solution. He said that the “working out specific agreements” should be done “in a dialogue with the United States and its allies.” He added, diplomatically, that “we aren’t demanding any special conditions for ourselves and realize that any agreements must take interests of Russia and all Euro-Atlantic countries into account.”
While this would obviously be the least confrontational path, it is the least likely to be be taken, as the only assurances being given today come in the form of Sec. of Defense Lloyd Austin, who recently reassured Georgia and Ukraine that the "door is still open" to NATO membership, much to the chagrin of Moscow.