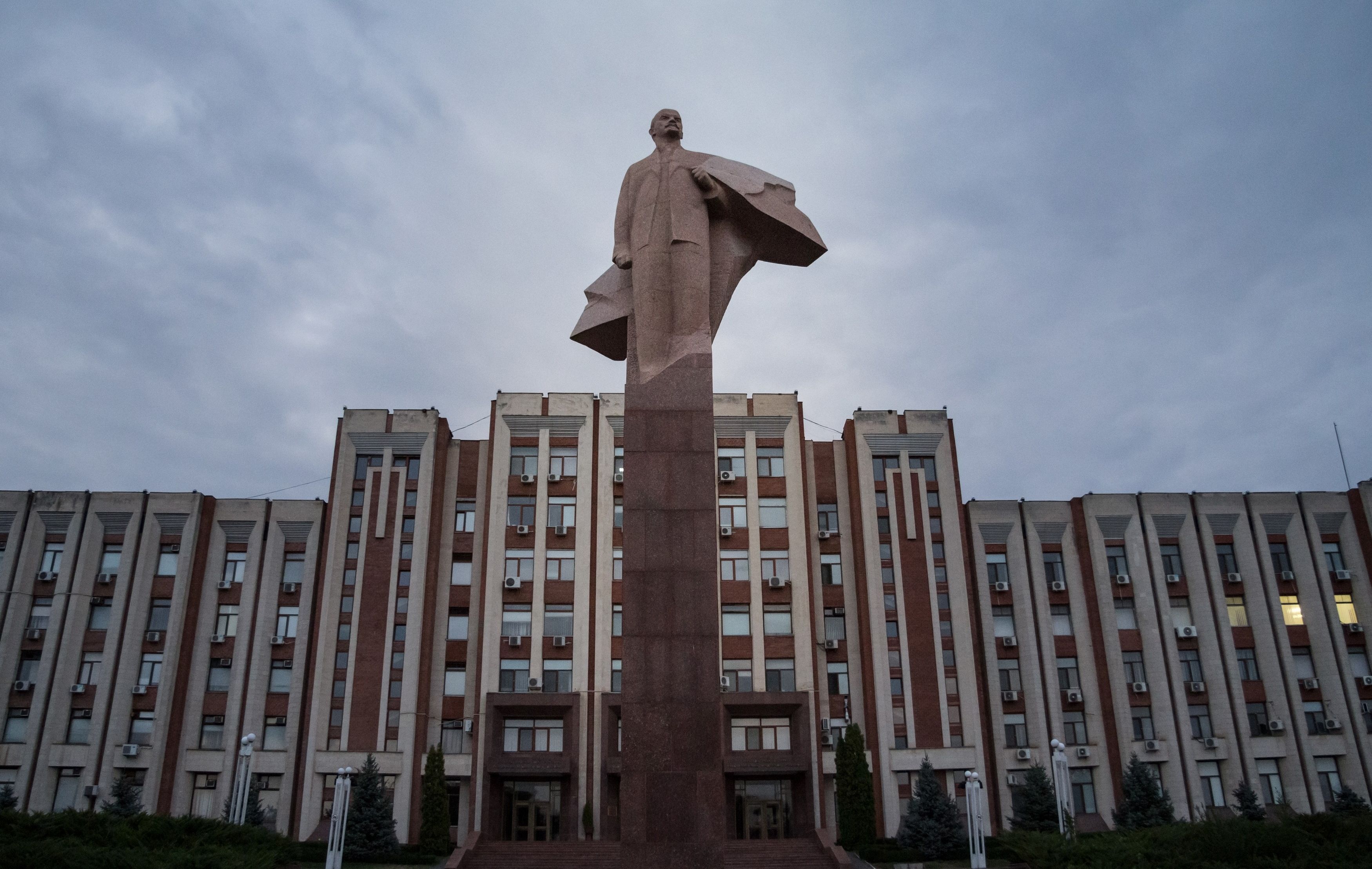
Tucked between Moldova and southwestern Ukraine is Transnistria, a Russian-backed separatist entity. Officially known as the Pridnestrovian Moldovan Republic, many describe this statelet as a Soviet time capsule. Transnistria’s capital, Tiraspol, is filled with Lenin statues, Soviet era architecture, and streets named after Karl Marx and famous Soviets while the Transnistrian flag features a hammer and sickle. Existing within Moldova’s internationally recognized borders, no U.N. member-state recognizes this breakaway republic’s independence — not even Russia.
Amid the USSR’s implosion in the early 1990s, Russian-speaking separatists in Transnistria feared growing Moldovan nationalism and the possibility of Moldova, which had just declared independence, reunifying with Romania. Russian troops and Cossack fighters helped Transnistrian paramilitary groups fight Moldovan forces in the Transnistria War (1990-92), which killed up to 700 people.
To this day the conflict remains frozen. Since 1992, officials in Moldova’s capital, Chișinău, and Tiraspol have prevented military clashes. Over the past three decades, the Moldova-Transnistria file has not concerned Washington too much. That is until recently.
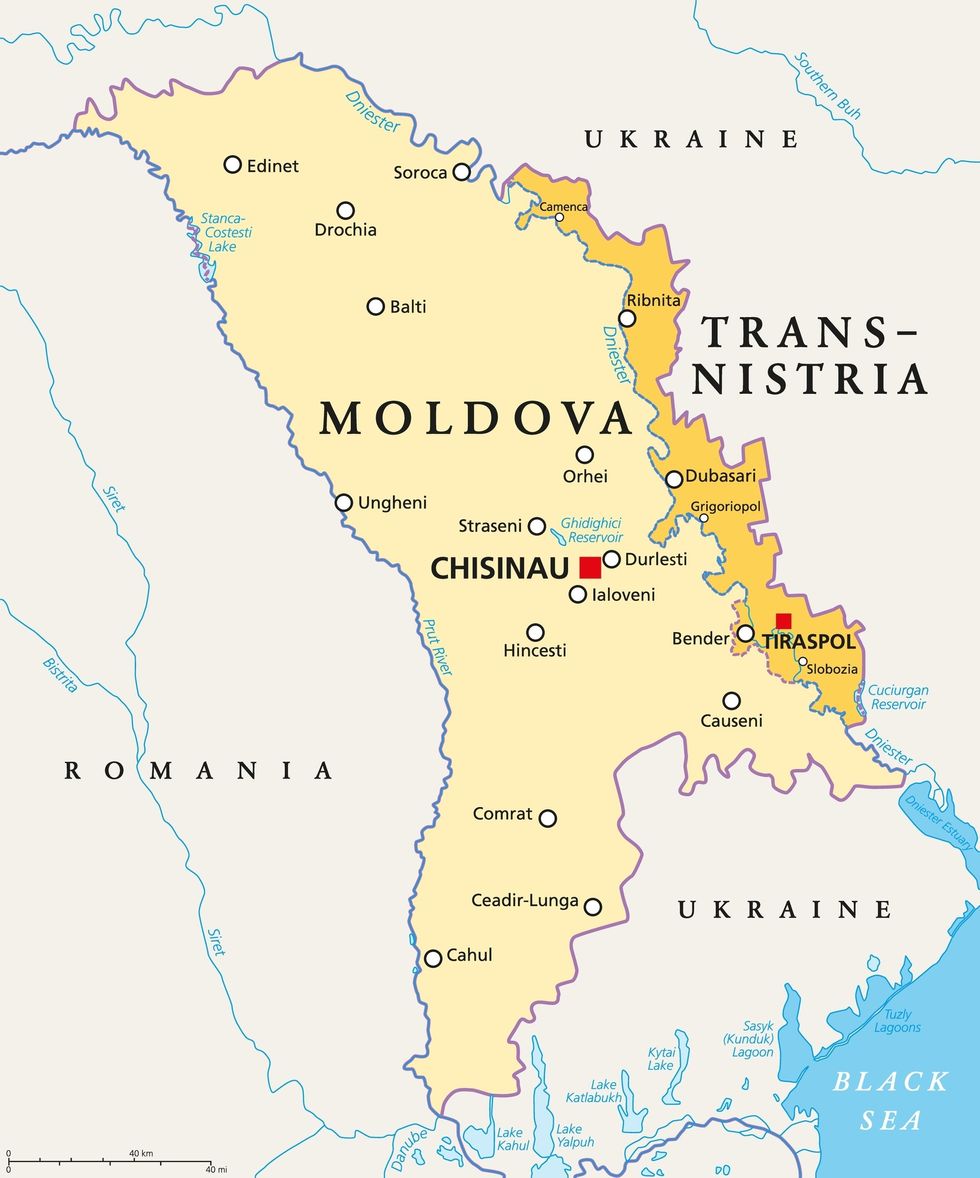
Russia’s full-scale invasion of Ukraine in February 2022 raised concerns about this frozen conflict unfreezing. Given that 1,500 Russian soldiers have been present in Transnistria as “peacekeepers” and as part of the Operative Group of the Russian Troops since the 1990-92 war, some analysts warned of Transnistria opening a second front against Kyiv while intensifying pressure on Chișinău. Such a scenario would risk Romania, which is linguistically, ethnically, historically, and culturally tied to Moldova, clashing with Russia — a high-stakes confrontation considering Romania’s NATO membership.
In April 2022, the acting commander of Russia’s Central Military District announced that Moscow sought to form a land bridge linking the Donbass to Transnistria. Doing so would have expanded the Ukraine war into Moldova’s internationally recognized borders and cut the Kyiv government off from access to the Black Sea, landlocking Ukraine.
Yet, Ukrainian forces prevented Russia from seizing Odessa and other parts of the would-be Donbass-Transnistria land bridge. Consequently, concerns in the West about Transnistria vis-à-vis the Ukraine war eased.
Last month, however, Tiraspol asked Russia for protection from the perceived threat posed by Moldova’s pro-EU government. In response to this call for Moscow’s protection, Russia’s Foreign Minister Sergey Lavrov said Chișinău was “following in the footsteps of the Kyiv regime” by “canceling everything Russian” and “discriminating against the Russian language.”
On March 17, a drone hit a military site in Transnistria, destroying a helicopter, which according to Moldova’s Bureau for Reintegration Policies “has not worked for several years,” and ignited a fire. Authorities in Tiraspol claimed that the Ukrainians waged this attack from Odessa. Both Kyiv and Chișinău denied any involvement in the military site explosion.
The Ukrainian government accused Moscow of being behind this “provocation in Transnistria with a kamikaze drone attack on a military base.”
Adding to this tension is the fact that on that same day a man threw two Molotov cocktails at the Russian embassy in Chișinău. At the time, Russian citizens in Moldova were at this diplomatic mission voting in their country’s presidential election. Moldovan authorities detained the individual, who was identified as a dual Moldovan-Russian citizen.
As of writing, the public has not been provided with any evidence to substantiate Tiraspol’s claims about Kyiv being behind the attack on the helicopter. If Ukraine carried it out, perhaps it was Kyiv’s warning to Moscow about the dangers of making any bold moves vis-à-vis Moldova-Transnistria in response to Tiraspol’s request for Russian protection from the U.S.- and EU- backed government in Chișinău. However, it is important to again stress that Ukraine’s responsibility for this episode has not been proven.
Meanwhile, some experts maintain that if Russia prevails in Ukraine, Moldova would be the next Eastern European country that Moscow attacks. “[Russia] has long used Transnistria and the separatists there, just like the ones in Donbass, as instruments to keep Moldova off balance and there are many other ways that Russia has destabilized, or tried to destabilize, Moldova,” Matthew Bryza, the former U.S. deputy assistant secretary of state for Europe and Eurasia, told RS.
“But Russia has no ability now to invade Moldova. Yes, it has a military base there. But I think Russia has enough on its plate right now in Ukraine and…unless it prevails Ukraine, it won’t do something similar in Moldova. But if it does succeed in Ukraine, I fear Moldova would be next,” added Bryza. However, the former U.S. diplomat emphasized that he does not expect Moscow to prevail in Ukraine.
A Russian invasion of Moldova-Transnistria does not currently seem to be an option for the Kremlin. Transnistria, unlike Ukraine and Georgia, does not border Russia and Moscow lacks the manpower to take control of the Ukrainian regions of Mykolaiv and Odessa. Nikola Mikovic, a Belgrade-based political analyst, does not believe that Russia could do in Moldova-Transnistria what it did in Ukraine beginning in 2014.
“Under the current circumstances, when Russia has a hard time capturing villages around Avdiivka in the Donbass, seizing Odessa is extremely unlikely to happen. Therefore, Russia does not have capacity to turn Moldova-Transnistria into its ‘next target,’ while Chișinău, firmly backed by the West, can destabilize the breakaway region at any time,” Mikovic told RS.
Although difficult to predict how a second Donald Trump administration would respond to Russian moves on Moldova-Transnistria, it can probably be taken for granted that the Biden White House would strongly back Chișinău under such circumstances. “It’s simply not possible with any degree of accuracy to predict now how the Biden administration would react if Russia invaded Moldova…other than the obvious which is there’d be strong U.S. support for Moldova and probably military assistance,” said Bryza.
“Moldova occupies an important geopolitical location on the borders of NATO and the EU, and NATO is very concerned about checking any potential Russian expansion westward. Also, it would not bode well for Ukraine if it were suddenly to face even a small number of Russian troops attacking it from the west,” John Feffer, the director of Foreign Policy in Focus, told RS.
“So, Moldova might become like Quemoy and Matsu, the tiny islands that Beijing tried to seize in the Taiwan Strait in 1958. Taiwan, like Ukraine, was the ultimate prize, but the islands were steppingstones, and the U.S. was determined to defend the little islands at all costs,” added Feffer.
Geography limits Russia’s means to maneuver vis-à-vis Transnistria. Thus, keeping the Chișinău-Tiraspol conflict frozen best serves Russia’s interests. Leveraging groups in Moldova with pro-Moscow sentiments such as the Gagauz minority to possibly change the government in Chișinău is a card which the Kremlin might possibly try to play. Either option could help Moscow further its agenda of preventing Moldova, which became an EU candidate in June 2022, from integrating into Western institutions, chiefly NATO.
“Russia wants to secure the perimeter of the ‘Russian world.’ But that doesn't have to be a firm border. It will be content to establish a zone of fragmentation that encompasses Georgia, Ukraine, and Moldova and that serves as a kind of moat to protect fortress Russia. This is not a reconstruction of the Soviet Union. It’s not a bid to confront NATO directly. But it nevertheless exacts enormous costs on the people of those fragmented countries,” offered Feffer.
To preserve the status quo in Moldova-Transnistria, “the Kremlin will almost certainly have to continue making behind-the-scenes concessions to the West and Ukraine,” commented Mikovic. “For instance, it’s entirely possible that Moscow provided ‘security guarantees’ to Kyiv that it will not strike the so-called decision-making centers in the Ukrainian capital, in exchange for Ukraine’s passive approach regarding Transnistria.”
The Serbian expert on Russian foreign policy noted that at any time NATO could coordinate with Kyiv to enable Moldova to bring Transnistria under Chișinău’s control through force. “For me, it’s a big mystery why Western policy makers and strategic planners have still not taken such an action,” Mikovic told RS.
A major win for Washington would be an unfreezing of the Moldova-Transnistria conflict with a potential joint Ukrainian-Moldovan operation defeating the Moscow-backed separatists. Yet, even if the West would back Kyiv and Chișinău in pursuit of such an outcome, there are no indicators that Moldova is considering such a military solution to this frozen conflict.
“For the foreseeable future, Chișinău will likely continue putting economic pressure on Tiraspol, aiming to weaken the breakaway region’s de facto independence, and force it to reintegrate into Moldova,” said Mikovic. “In the long-term, though, a military conflict should not be ruled out.”
- A looming crisis in Moldova's breakaway state ›
- Washington should resist the urge to get involved in Moldova | Responsible Statecraft ›














