One of the most critical arms control agreements, the New Strategic Reduction Arms Treaty (New START), will disappear soon if leaders do not step up to save it. New START imposes limits on the world’s two largest nuclear arsenals, Russia and the United States, and remains one of the last arms control agreements still in effect. Those limits expire in exactly one year from Wednesday, and without it, both stockpiles will be unconstrained for the first time in decades.
Democrats in Congress already express consistent support for the extension of New START, turning the issue into a Democratic Party agenda item. But today’s hyper-partisan landscape need not dictate that arms control must become solely a Democratic priority. Especially when the treaty in question still works, provides an important limit on Russian nuclear weapons, and ultimately increases our national security.
Historically, Republican administrations have championed nuclear arms control agreements.
Since the end of the Cold War, both Republican and Democratic administrations worked to reduce the number of nuclear weapons in the world. But Republican presidents actually developed more arms control agreements to reduce the quantity of nuclear weapons than Democratic presidents. The Trump administration could easily extend New START without major revisions and continue the legacy of the GOP.
Beginning with the Nixon administration following through to the administrations of President Ronald Reagan, George H.W. Bush, and George W. Bush, Republican administrations all pursued arms reduction treaties with Russia in an effort to curtail Russia’s nuclear arsenal. From 1969 to 1972, the Nixon administration negotiated the Strategic Arms Limitation Talks (SALT I) where both sides pledged not to construct new Intercontinental Ballistic Missile (ICBM) silos or increase their size, and capped the number of Submarine-Launched Ballistic Missile (SLBM) launch tubes and SLBM-carrying submarines. This agreement also included the Anti-Ballistic Missile (ABM) Treaty which limited strategic missile defenses to 200 (and later 100) interceptors each.
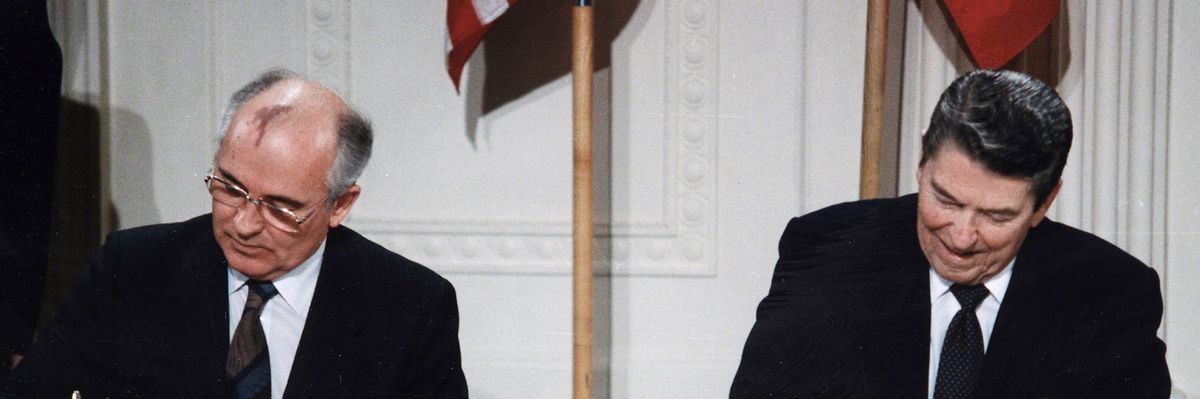
In 1982, the Reagan administration presented the Strategic Arms Reduction Treaty (START), which sought to reduce the number of nuclear weapons in the worldwide stockpile by limiting overall warhead counts to 6,000 and delivery vehicles to 1,600. While Reagan would not remain in office long enough to conclude negotiations, other Republican presidents continued the START structure. Reagan did, however, sign the Intermediate-Range Nuclear Forces (INF) Treaty in 1987, agreeing to eliminate the ground-launched, mid-range nuclear missiles. This was the first agreement to reduce nuclear arms while also introducing important and comprehensive verification measures.
The Republican legacy of arms control continued under both Bush presidencies, with George W. Bush negotiating and implementing START II, which reduced U.S. and Russian strategic forces to 3,500 warheads, and the Moscow Treaty, which eliminated roughly two-thirds of the two countries’ nuclear warheads over ten years.
The Obama administration built New START on the existing models and the Senate ratified the treaty with hard-fought bipartisan support. New START’s original ratification promoted the bipartisan concept that “politics stop at the water’s edge,” as should its extension now.
In today’s Congress, standalone bills by Reps. Eliot Engel and Michael McCaul and Sens. Todd Young and Chris VanHollen indicate the bipartisan support for New START extension lives on. The Engel-McCaul bill boasts three Republican and eight Democratic co-sponsors, and the Young-Van Hollen garnered co-sponsors from two Republican senators and one Democrat so far.
The bipartisan cooperation continued in the effort to save New START during conference negotiations to finalize the fiscal year 2020 National Defense Authorization Act (FY20 NDAA). If the Trump administration decides to withdraw from the treaty, it must provide a 120-day congressional notice. Both Republican and Democratic leadership established this early-warning framework because of their common concern over New START’s status.
Even Republican constituents want to limit nuclear weapons worldwide and overwhelmingly support the extension of New START. Over 65 percent of voters in every state call for New START extension.
Scholars and experts at conservative think tanks like the Heritage Foundation agree that “nuclear arms control aims to diminish the likelihood of nuclear conflict” if “Trump channels Reagan on the path to arms control.” The American Enterprise Institute published work openly supporting New START extension as in the country’s strategic interest. As this issue garners popularity among republican constituents, validators, and leaders, the Trump administration should not dismiss the merits of the treaty as yet another “bad deal” brokered by Democrats.
The legacy of Republican administrations after the Cold War illustrates their efforts to maintain a consistent level of arms control while pursuing quantitative reductions to Russia’s nuclear arsenal. President Putin at the end of last year stated that “Russia is willing to immediately, as soon as possible, before the year is out, renew this treaty without any preconditions.” Considering that New START is the last guardrail preventing a possible arms race and nuclear instability with Russia, the Trump administration must weigh carefully any decision regarding the treaty’s future.