Johnny Harris, a popular YouTuber with nearly 6 million subscribers, published a video on Thursday that sought to answer an enormous question: “Why does the U.S. spend so much on its military”? He answers that question in extreme detail and ultimately arrives at uncovering why, in large part, the Pentagon budget is so high: the corrupt process of how lawmakers and big defense contractors and their lobbyists are all on the take.
The first half of Harris’s deep, 28 minute long dive into the U.S. military budget focuses on what the Pentagon is actually paying for, things like troops’ salaries and health care, operations and maintenance, bases, construction, and research and development. He notes that the Defense Department is so big and complex, it has never been able to pass a financial audit.
“The U.S. is not a normal country with a regular military,” Harris says, by way of offering a kind of explanation as to why the Pentagon spends so much on all these things. “The U.S. is a global hegemon who uses its military to assert control and order over every corner of the globe,” he adds, in effect, flagging American primacy as a culprit.
“But there’s another reason why this budget is so high and this reason is much more infuriating to me,” Harris says. ”Most of this money is going to private corporations.”
Harris then spends the rest of the video breaking down our country’s corrupt procurement processes, starting with weapons companies. “We’ve got kind of a monopoly issue on our hands,” he says, noting how dozens of weapons contractors consolidated themselves down to five big corporations. “For this reason the prices can get pretty out of control.”
Dr. Heidi Peltier, Senior Researcher at the Watson Institute at Brown University and Director of the Costs of War Project, then tells Harris about how, because of their monopoly, weapons contractors can engage in severe price gouging practices. “The Department of Defense has found routinely that there’s overcharging through corruption and waste and fraud,” she said, which, in part, has resulted in 40-50% profit margins.
For example, the Pentagon, Harris notes, paid Boeing $3,357 for one ball bearing, a part it could have gotten for $15. Harris then details how all the corruption works:
- The big five contractors — Boeing, Lockheed Martin, General Dynamics, Raytheon (now RTX) and Northrop Grumman — are “doing whatever they can to make sure the money keeps flowing to their companies” with lobbying and campaign contributions.
- The revolving door: “In 2022 top defense companies hired 672 employees directly out of the Pentagon to work as lobbyists, board members and executives,” Harris says. According to Peltier: Contractors “promise a good, high paying job after that government official is out of government and so the government official has an incentive to give a generous contract to the contractor.”
- Lawmakers’ profit: “To add insult to injury here, some of the lawmakers who approve the Pentagon’s budget own stocks in the defense contracting companies,” Harris says. “The lawmakers get richer if we spend more money on defense,” he adds, noting that this is a clear conflict of interest: “We should not do this. This is not a thing we should do.”
- Lawmakers’ incentive for re-election: Harris then explains how defense contractors “intentionally allocate their operations all across the country” so “lawmakers are incentivized to keep these contractors making stuff in their district to provide jobs for their people so they can keep getting elected.”
Harris then highlights Sen. Roger Wicker as an example of a member of Congress who often pushes for more money for the Pentagon, which in turn goes to weapons companies, who then lobby Congress and make campaign contributions so lawmakers can tell their constituents they’re diverting federal funds to their districts to protect (or create) defense jobs:
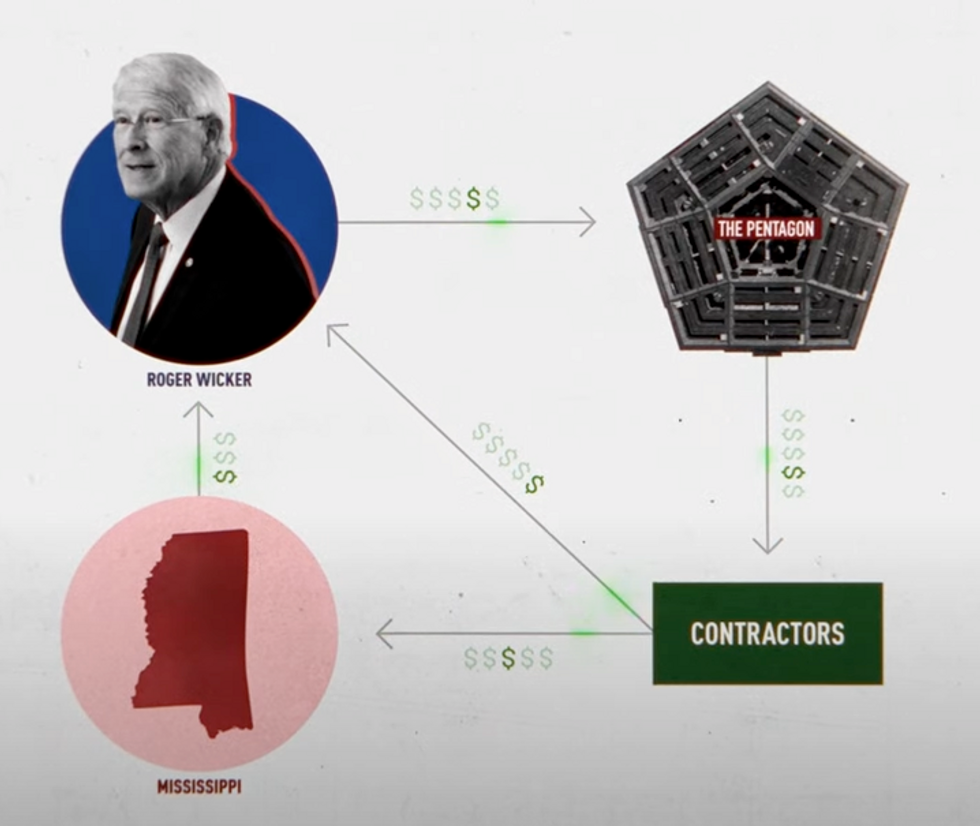
“It is this system that has created an environment where there is very little political pushback to the endless ratcheting up of our military budget,” Harris says. Watch:
- Congress stuffs $25 billion into Pentagon contractor stockings ›
- Another year, another delusional Pentagon budget request ›
- Pentagon can't account for 63% of nearly $4 trillion in assets ›
- Biden's new whopping $886B defense budget request ›
- Congress is crying wolf again on the Pentagon budget ›
- Trump's DOD spending order sounds good, but read the fine print | Responsible Statecraft ›
















