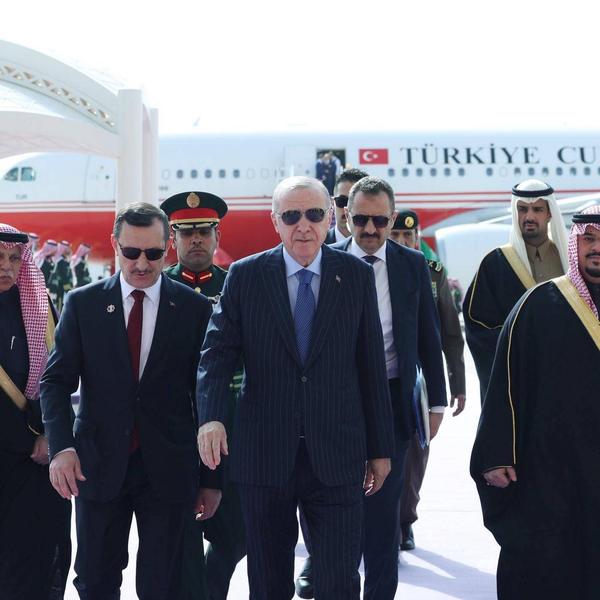
The NATO Innovation Fund, the “world's first multi-sovereign venture capital fund,” made its first investments earlier this summer in deep tech companies including British aerospace manufacturing company Space Forge and AI companies ARX Robotics and Fractile.
Modeled like the U.S. intelligence community’s venture capital arm IQT (In-Q-Tel), the fund’s intention is to focus on spurring innovation in areas including biotechnology, AI, space tech, and advanced communications.
As NATO Innovation Fund Board Chairs Klaus Hommels and Fiona Murray described the project's purview in Fortune in July: “By investing in and adopting emerging dual-use technologies, NATO can leverage the private sector’s innovation power and its transatlantic talent pool, while countering our strategic competitors’ influence and ambitions.”
Fund leadership believes that venture capital’s propensity for technological innovation can be NATO’s trump card in an increasingly perilous geopolitical context. But taking after the likes of venture capitalists isn’t exactly a recipe for global security and peace. If American VCs’ hawkish track record is any indication, rather, it’s one that promises to supercharge militarism on a transnational scale.Venture capital’s defense break
NATO Innovation Fund proponents propose that VCs take on the financial risk they perceive as necessary to develop cutting edge security- and defense-tech, which has lagged in places like Europe due to regional difficulties bringing start-ups to scale.
Venture capital is indeed a risky business, where VCs burn through large sums of money on smaller start-ups in a bid to grow them into large companies. If the companies they've invested in go public, VCs can then cash in on often extremely high rates of investment returns, sometimes worth hundreds of times their original investment.
When introduced to the defense space, however, VCs’ hunger for such investment returns ultimately puts ethics on the backburner in favor of gaming a primary client — governments — to produce business-sustaining contracts, supercharging militarism in the process.
Able to withstand the high failure rate of VC-backed startups due to their gargantuan wealth, controversial American VCs like billionaire investor Peter Thiel and former Google CEO Eric Schmidt have spawned defense tech industry heavy hitters like Anduril, Rebellion Defense, and Hadrian, all while steering more tech companies towards developing more military applications for their products.
These VCs and the companies they’ve funded have honed tangible political power in the process, from funding successful congressional campaigns (including current Republican vice presidential nominee JD Vance’s previous 2022 U.S. Senate campaign) and launching associates into positions in presidential administrations, to extensive DC lobbying and securing top-dollar military contracts.NATO’s VC plunge
American VC-backed defense tech companies are raking in monstrous profits amid bloody conflicts in Ukraine, Gaza and beyond; the NATO Innovation Fund’s creation suggests outside VCs want in.
But to hope these VCs and the respective tech and defense startups they spawn won’t attempt to game the system for funds and influence like their American counterparts is foolhardy. Defense companies are increasingly lobbying EU officials in Brussels; prominent Thiel-backed AI research company OpenAI, meanwhile, is already lobbying against AI regulations in the European Union.
And while founded by NATO and funded by the contributions of two-dozen NATO states, the NATO Innovation Fund isn’t technically even NATO’s. Rather, the NATO Innovation Fund states on its website that it’s a privately owned, for-profit venture capital fund given permission to use the NATO name. NATO “is not invested financially or involved in [the Fund’s] decision-making.”
The Fund’s operations, in other words, appear opaque despite its possible impact on NATO’s military- and security-related capacities. Generally, NATO and associated projects’ funding arrangements suffer from a lack of transparency due to NATO’s complex, transnational composition and organization, which Stockholm International Peace Research Institute (SIPRI) Editor Dr. Ian Davis fears invites “potential for ‘unwarranted influence’ by the military–industrial complex.”
As Ingrid Lunden highlighted in TechCrunch last year, it’s unclear whether there are any red lines regarding the types of companies the Fund would support or otherwise collaborate with. In this respect, American-based VCs’ abject lack of guardrails, where VCs have consistently invested in controversial AI-powered military technologies like lethal drones and military targeting systems, inspires little confidence.
Power competition through venture capital
Critically, the NATO Innovation Fund has been created in the name of great-power competition. Upon the Fund’s creation in 2022, NATO Secretary General Jans Stoltenberg emphasized a need for a technological edge against NATO’s adversaries: “Nations that do not share our values, like Russia and China, are challenging [our technological] lead in everything from Artificial Intelligence to space technologies…We [must] do everything in our power to remain at the forefront of innovation and technology.”
In December 2022, Atlantic Council nonresident senior fellow and former NATO Assistant Secretary General Giedrimas Jeglinskas even proposed that NATO-allied countries in Asia set up NATO Innovation Fund-aligned venture capital funds in a team effort to counter China.
Such language suggests that great-power competition and tech war rhetoric, are likely to worsen relations with countries, notably China and Russia, rather than improve them, and will heighten if North Atlantic-based VCs garner increased political influence via organizations like the NATO Innovation Fund.
Despite fraught circumstances, 24 NATO states are backing the Fund. And the European Investment Fund, which has also been working to bolster defense-focused VCs through efforts like its Defence Equity Facility, is now partnering with it.
Simultaneous efforts across the North Atlantic, meanwhile, are slated to further intertwine transnational defense with Big Tech. As an example, NATO’s DARPA-style Defense Innovation Accelerator for the North Atlantic (DIANA), proposed in 2021 and made operational in 2023, has expanded in recent months, more than doubling its accelerator sites and test centers.
In addition to a European Defense Fund with a nearly $9 billion budget from 2021-2027, the European Union also unveiled the first ever European defense industry strategy to bolster military capacities earlier this year.
Prioritizing acquiring military might over genuine diplomacy, NATO’s recruitment of profit-minded VCs signals turbulent times are ahead.