In the midst of Israel’s destructive campaign in the Gaza Strip, which has killed at least 34,000 people to date, Congress recently approved a $15 billion U.S. military aid package to Israel.
Providing funds towards artillery and munitions development, replenishing defense systems, and Gaza aid, the package also includes $1.2 billion towards Israel’s sci-fiesque “Iron Beam” laser weapon, a prospective directed energy system for air defense.
Once operational, Iron Beam’s systems appear slated to revolutionize Israel’s defense capacities, escalate the ongoing crisis in Gaza and already boiling tensions in the Middle East, and normalize lasers’ use in warfare as efforts towards directed energy weapons (DEWs) intensify. What’s more, the U.S. seems interested in procuring Iron Beam and adjacent technologies to its own ends, perhaps facilitating DEWs’ further future proliferation.
What is Iron Beam?
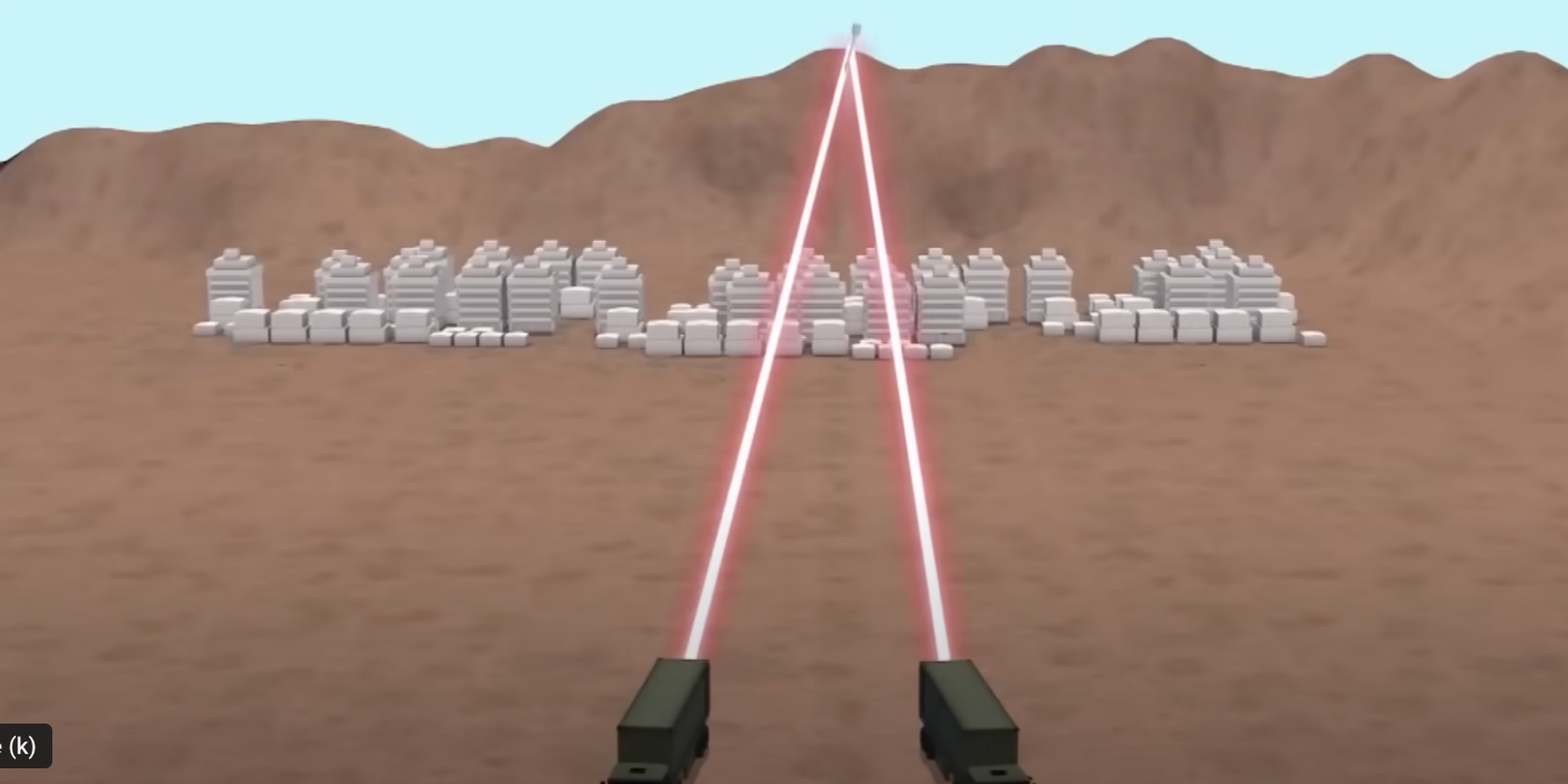
A prospective successor to Israel’s “Iron Dome” missile defense system, which launches missiles to intercept and shoot down incoming threats within Israeli borders, Iron Beam is a directed energy system that neutralizes or brings down incoming projectiles with a fiber laser.
While Israel claims Iron Dome eliminates 90% of incoming threats, the system’s weakness is its higher costs, where a single interceptor missile costs about $50,000. In contrast, Iron Beam would produce similar results without costly artillery, running solely on electricity to produce laser beams that have destroyed tanks, rockets, drones, and other targets in tests.
"[Iron Beam] is a game-changer because we cannot only strike the enemy militarily but also weaken it economically," former Israeli Prime Minister Naftali Bennett remarked back in 2022, explaining that with Iron Beam, “[Israel’s adversaries can] invest tens of thousands of dollars in a rocket and we can invest two dollars to cover the cost of the electricity in shooting down the rocket."
Bad weather can blunt the system’s effectiveness, however, which means Iron Beam is perhaps best used in tandem with the Iron Dome system for comprehensive air defense.
A growing interest in Directed Energy Weapons
Israel’s Iron Beam is a manifestation of governments’ decades-long interest in DEWs, systems that can convert chemical or electrical energy into radiated energy that can be focused to damage, destroy or neutralize adversarial targets. Operating at rapid speeds, directed energy weapons such as lasers, high-power microwaves, and particle beam weapons are crafted to discreetly, quickly, and precisely hit targets without artillery.
Aware of their potential, a number of countries are developing DEWs. The UK recently tested its “DragonFire” laser weapon, which reportedly can hit a coin from a kilometer away. And Russia’s Peresvet laser system, designed to disable or “blind” high-altitude spacecraft, like satellites, and the Zadira laser system, which can shoot down drones, further, are being tested on Ukraine’s battlefields.
Likewise, the U.S. spends about $1 billion annually to develop laser and adjacent directed energy weaponry. Notably, the U.S. Army’s Rapid Capabilities and Critical Technologies Office is overseeing an Indirect Fire Protection Capability-High Energy Laser prototype program, awarding Lockheed Martin with a contract for the project in October 2023. Once operational, the laser is designed to counter or neutralize rockets, artillery, mortars and other projectiles hostile to warfighters in tandem with a military’s other defense components.
Ultimately, DEWs offer a cheap, accurate solution for militaries looking to counter drones and other aerial threats. But their destructive capacities, where Iron Beam’s lasers are able to neutralize and destroy many projectiles with a simple laser fire, are clear and contribute to an ever more perilous future for warfare.
Military aid to Israel accelerates DEW proliferation
Iron Beam’s pending operationality, whose deployment is reportedly being expedited by manufacturer Rafael Advanced Defense Systems, poses heightened dangers within the context of Israel’s ongoing destruction of the Gaza Strip. Although Iron Beam was created for defensive purposes, Israel could plausibly repurpose its lasers as offensive purposes. Indeed, Israel has previously utilized other controversial and experimental weapons systems in Gaza, such as its new AI-powered Gospel and Lavender systems for military targeting.
Meanwhile, just as the U.S. had purchased batteries for Israel’s Iron Dome in the past (after October 7, it leased the two Iron Dome missile systems it purchased back to Israel), the U.S. is considering procuring Iron Beam for itself, suggesting that U.S. military aid to Israel is not only about assisting an ally, but also about expanding and upping U.S. military capacities.
Ultimately, U.S. military aid to Israel enables and exacerbates its campaign against the Palestinian people while fueling prospects for greater conflict in the region. When applied towards projects like Iron Beam, moreover, such funds assist the introduction and normalization of consequential and destructive weapons systems within military contexts without substantive public debate.
- Will US troops be drawn into the Israel-Gaza war? ›
- Don't take your eyes off Gaza ›
- Top Dems sign off on biggest weapons sale to Israel to date | Responsible Statecraft ›
- Trump doubles down on wasteful American Iron Dome | Responsible Statecraft ›
- Israeli wants to put 'Iron beam' laser on Trump’s Golden Dome | Responsible Statecraft ›



 Screengrab via niacouncil.org
Screengrab via niacouncil.org Screengrab via niacouncil.org
Screengrab via niacouncil.org











