On Friday, U.S. officials said that the pier built in May to distribute humanitarian aid into the Gaza Strip was once again suspending operations — this time potentially for good.
The Biden administration has praised the project, but critics have called it “humanitarian theater,” and a "failure," as it's proven to be wholly inadequate for providing assistance to Gaza, where famine is looming and hospitals are unable to operate.
RS has been raising concerns about the project, mainly the costs, dangers, and lack of effectiveness associated with it. Moreover, asking why the White House chose this risky option instead of the far simpler solution of pressuring Israel to open humanitarian crossings and protect aid workers inside the Strip.
Today we let the numbers associated with this seemingly ill-fated venture do the talking:
69: It took 69 days in between Biden’s announcement during the State of the Union that the U.S. military would build “temporary pier in the Mediterranean on the Gaza coast that can receive large ships carrying food, war, medicine and temporary shelters … and ensure that humanitarian workers aren’t caught in the crossfire,” and the day that the pier was completed. Two days after construction concluded, on May 17, the first trucks rolled down the pier.
4: The U.S. was forced to halt operations 4 different times since May 17, mostly due to weather events. Operations were suspended between May 28 and June 7; June 9-10; June 15-20; and finally on June 28.
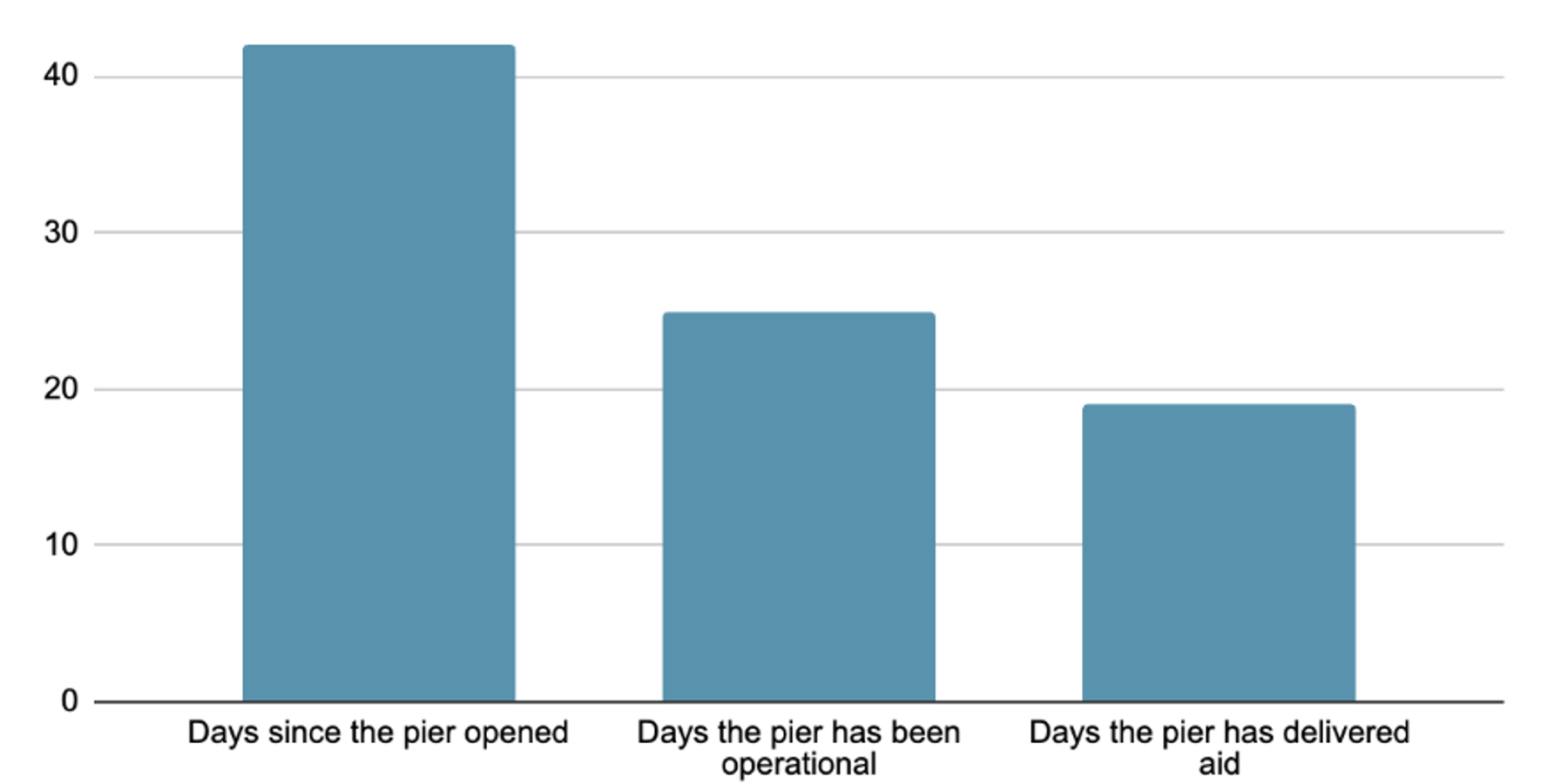
47 and 25, and 19: In the 47 days since the pier was built it was only operational for 25 of them, and aid only came in, at most, on 19 of those days.
That means that the U.S. military only delivered aid through the port for less than half of the total possible days.
For a significant portion of this timeframe — between June 9 and June 28 — the U.N. World Food Programme did not distribute any of the goods that were piling up on shore, due to fears that they could be targeted by Israeli air strikes and other security fears.
19.4: The pier was used to get approximately 19.4 million pounds of food into Gaza. It is unclear exactly how much of that aid has made its way to the suffering population — though a “vast majority” of it was never distributed.
NBC News reported on the day that the U.N. resumed food distribution that roughly 15 million pounds of food and other aid materials had accumulated on the shore during the days when the pier was operational but no aid was being given to Gazans. If this total was included in the 19.4 million pound estimate, that means that as little as 4.4 million pounds may have actually been moved into the Strip.
Even if the entirety of 19.4 million pounds had been distributed to the people, that would still represent a far from sufficient total. Based on past estimates from both the Israeli government and UNRWA, 19.4 million pounds would translate to roughly 646 truckloads in the last month and a half. Experts have said that somewhere between 300 and 600 truckloads worth of aid are needed every day in order to avoid a full-blown famine in Gaza.
320 (or 230): When the construction for the pier began in April, the Pentagon anticipated a $320 million price tag to build it and operate it for 90 days. In June, DOD revised the estimate down to $230 million, because “costs for contracted trucks, drivers and commercial vessels were lower than expected and the United Kingdom contributed a berthing vessel for soldiers and sailors.”
The final figure could end up being slightly different, since the pier has undergone a series of repairs (the first set of repairs cost roughly $22 million), and because, if operations are indeed halted, the pier would have operated for less than half of the original 90-day plan.
- Mission creep: Will pier become a beachhead for US in Gaza? ›
- Staging ground for US military aid pier in Gaza attacked ›