The Biden administration wants you to believe the U.S. is leading international efforts to get humanitarian relief into Gaza and that supplies are “flowing to Palestinians” via the military’s pier operation there.
On Monday, Pentagon spokesman Maj. Gen. Pat Ryder announced that to date,1,573 tons of aid had been delivered from the pier to the beach, including 492 tons since it reopened on Saturday after some bad weather knocked it out of commission last month.
But supplies from the pier aren’t flowing to Palestinians, and never really have.
Hardly any food from the pier on the Gaza coast has actually reached starving Gazans since it became operational on May 17. The World Food Program (WFP) said only 15 trucks from the pier reached its warehouse inside Gaza for distribution from May 17-18, and that no aid came from the pier from May 19–21.
In Rafah specifically, no aid will reach Palestinians in need so long as Israel’s military offensive persists. WFP halted all deliveries to Rafah on May 21 due to Israel’s invasion of the city.
In addition, on Sunday, the WFP announced that it “paused” distribution of any more humanitarian aid from the pier due to security concerns after a U.S.-backed Israeli operation killed nearly 300 Palestinians the day before. WFP is the U.N. agency in charge of coordinating deliveries from the pier into Gaza.
The 492 tons of aid the Pentagon just boasted about will sit in warehouses on the beach until further notice. Meanwhile, the U.N. says that all humanitarian operations in Gaza are on the brink of collapse.
The reality is that the $320 million (revised more recently down to $230 million) “maritime humanitarian corridor” that Biden first announced during his State of the Union address in March is not working, at least not for Palestinians. It does serve the Biden administration’s interests by making it look like the U.S. is “doing something” for the civilian population while supporting an Israeli policy that destroys and starves it. The pier, in essence, provides humanitarian cover for an inhume policy.Pier one imports
Biden administration officials argue the pier isn’t a failure or public relations stunt but critics disagree.
On May 17, the first day the pier was operational, former USAID official and current president of Refugees International Jeremy Konyndyk said, “The pier is humanitarian theater. Much more about political optics than humanitarian assistance. … [T]he president is tweeting about a humanitarian gimmick while actual humanitarian capacity in Gaza grinds to a halt.”
On May 23, in response to a press question about Konyndyk’s comments, director of USAID’s Levant humanitarian response Dan Dieckhaus said, “You know, I would not call within a couple of days getting enough food and other supplies for tens of thousands of people for a month theater…everyone's entitled to their opinion, but I think we are already making a meaningful contribution to the overall effort.”
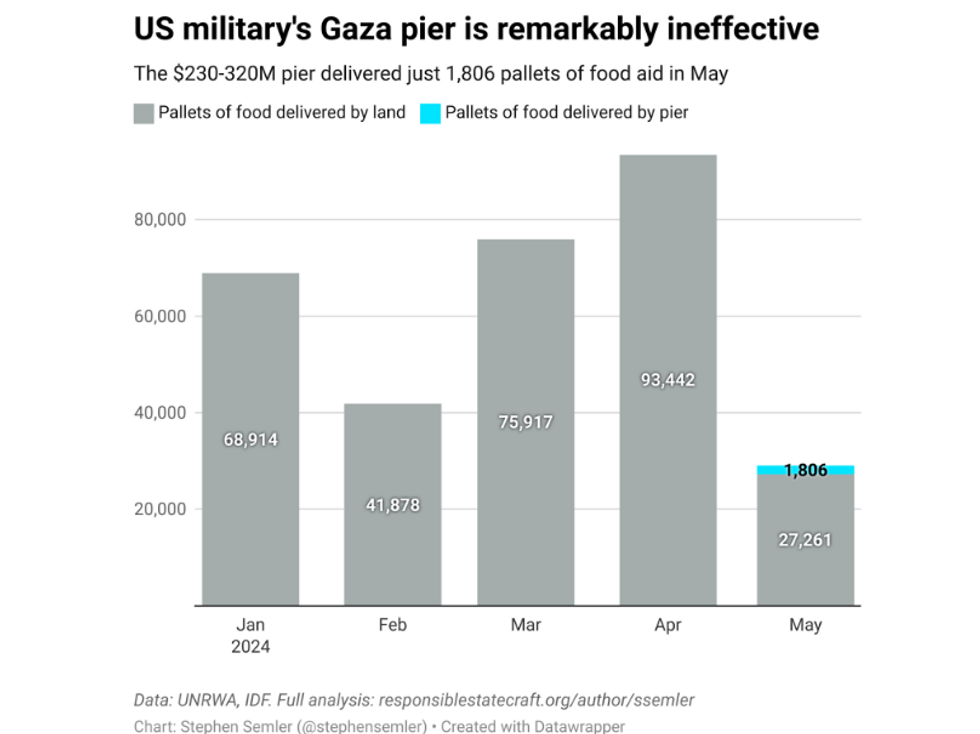
But according to U.N. humanitarian aid data of food imports into Gaza from January through May, far more food aid reached Gazans before the U.S. pier opened. On May 7, Israeli forces closed the Rafah crossing as part of its invasion of the city. By the end of the month, 66,181 fewer pallets of food reached Palestinians in May compared to April. The pier, which opened May 17, didn't come close to compensating for this shortfall: According to the IDF, just 1,806 pallets of food from the pier reached aid agency centers in Gaza before it broke apart in a storm on May 25.
Meanwhile, food and other aid is piling up outside Gaza at the Rafah land crossing.
Not enough food was getting into Gaza before Israel closed the Rafah crossing, either. Through March of this year, monthly food imports into Gaza were virtually identical to what they were in 2022, even though food needs are five times higher now than they were then. The U.N.’s humanitarian response plan for Palestine in 2022 implemented $226 million for food security and nutrition. Requirements for those sectors in 2024 stands at $1.1 billion.
Political optics
A new report from the U.N. Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) and World Food Program concluded that 1.1 million Palestinians could face starvation by mid-July primarily because of “the devastating impact of the ongoing conflict” and “the heavy restrictions on access and goods.” The Biden administration enables the first problem by shipping weapons to Israel every 36 hours and tolerates the second by refusing to use the leverage those shipments afford to stop Israel from obstructing aid.
Some deny that that leverage exists, but Biden has already demonstrated that it does. On October 9, Israeli Defense Minister Yoav Gallant announced a “complete siege” of Gaza, pledging that, “there will be no electricity, no food, no water, no fuel. Everything will be closed.”
A couple weeks later, Gallant was pressed by Knesset lawmakers on why he agreed to let a trickle of aid in from Egypt. Gallant replied, “the Americans insisted and we are not in a place where we can refuse them. We rely on them for planes and military equipment. What are we supposed to do? Tell them no?”
Israel’s reliance on arms and political protection from the United States puts Biden in an extraordinarily powerful position to influence what Israel does and doesn’t do in Gaza. The current conditions on the ground reflect Biden’s policy choices. Currently, Israel is bombing civilian centers using U.S.-made munitions, while getting aid to Palestinians in need is “almost impossible,” and famine is imminent in Gaza everywhere it isn’t already happening.
Rather than change these conditions with a phone call to Israeli leadership, Biden told the U.S. military to build a pier.
There’s no time for humanitarian theater, according to the FAO/WFP report: “In the absence of a cessation of hostilities and increased access, the impact on mortality and the lives of the Palestinians now, and in future generations, will increase markedly with every day, even if famine is avoided in the near term.”
- US pier operations suspended as parts break off in 'high sea states' ›
- Alarming lack of detail in military's Gaza aid project ›
- US groups urge Biden to reverse course on Israel | Responsible Statecraft ›
- How Israelis admit to war crimes in Gaza without saying it | Responsible Statecraft ›
- US Gaza pier op was more than a flop, it was a gigantic hazard | Responsible Statecraft ›














