It is time for the Biden administration to level with the American people about the Ukraine war.
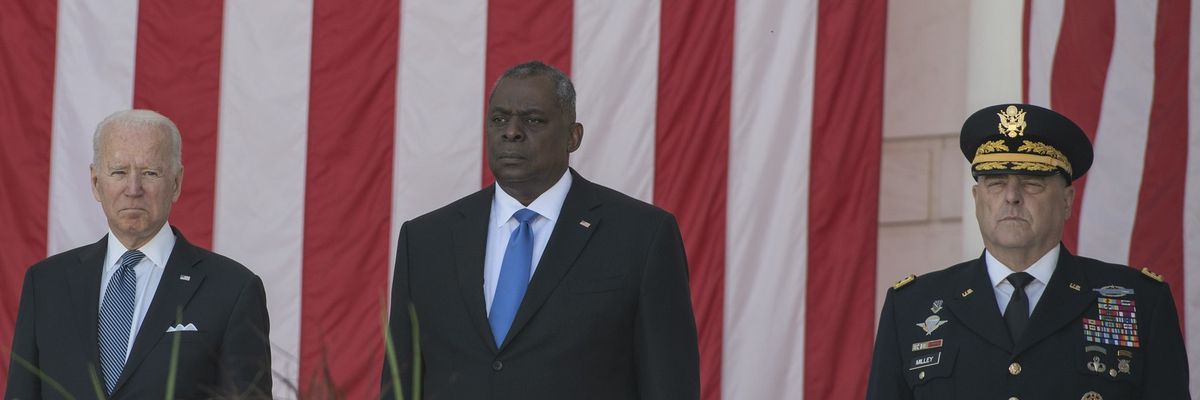
For more than a year, the White House has painted for the public a rosy picture of battlefield and strategic success. “Ukraine will never be a victory for Russia,” President Biden proclaimed during his visit to Kyiv in February. "We believe that we can win — they [the Ukrainians] can win if they have the right equipment, the right support," said Defense Secretary Lloyd Austin.
Secretary of State Tony Blinken has repeatedly insisted that the war will be a “strategic defeat” for Russia that will leave it weakened and incapable of future aggression. Even the administration’s most sober-minded observer of the war, Joint Chiefs of Staff chairman Mark Milley, has asserted that Ukraine has the leadership and morale to beat Russia.
Driven by these optimistic pronouncements, Biden officials have insisted that justice must prevail in the war. They say that Putin and other Russian officials must be tried for war crimes. They insist that, as the victim of unprovoked Russian aggression, Ukraine alone has the right to determine whether to seek a settlement or concede territory.
The bottom line from White House has been that American resolve will not waver and that the war will result in a uniformly happy ending for the United States and its allies: a “democratic, independent, sovereign and prosperous Ukraine,” a chastened and defanged Russia, and a “peaceful and stable Europe.” And all can and will be achieved without committing U.S. troops to fight against Russia and risking what Biden has called “World War Three.”
The purported leaks of classified documents, officially unconfirmed but covered widely in Western media, raise profound questions about this narrative. If these press reports are accurate, they suggest that the United States is tip-toeing much closer to a direct war with Russia than the Biden team has acknowledged.
They also allege that as of March there were a small number of undisclosed American Special Forces personnel are on the ground in Ukraine, raising the question of what Washington would do should Russians intentionally or unintentionally strike them. The West also quite literally dodged a missile strike when a Russian fighter jet mistakenly believed it had received approval to fire on a British intelligence collection aircraft, only for the missile to fail after the launch.
Moreover, the reports paint a much bleaker picture of Kyiv’s prospects in the war than the White House has acknowledged. They depict manning and training levels for Ukraine’s much anticipated counter-offensive that inspire little confidence it will produce a decisive breakthrough against reinforced Russian defenses. They warn that Ukraine is dangerously close to running out of air defense missiles, which have been vital to defending Ukrainian cities and infrastructure from missile and air attacks and —even more significantly — to preventing Russia’s air force from providing close air support to its ground forces.
These training and supply problems cannot be easily or quickly resolved. Ukraine has unquestionably fought well to this point in the war, but it has lost many of its most experienced and most effective fighters. Training tens of thousands of replacements takes significant time. Mastering sophisticated and unfamiliar weapons systems, learning to maintain them, and integrating them into battlefield operations is an enormous challenge.
And although the West has done its best to prepare Ukrainians for their counter-offensive, it does not have sufficient stores of artillery shells, anti-tank weaponry, and air defense missiles to sustain the war effort indefinitely, and it cannot ramp up military production lines quickly. Fulfilling Biden’s vow to support Ukraine “for as long as it takes” is a matter of capacity, not just political will.
The implications of Ukrainian attrition are potentially grave. Should the counter-offensive fail to break through Russian defenses, a Ukrainian military that is running short of trained reserves, artillery shells, and air defense missiles could be vulnerable to new Russian advances that are supported for the first time in this war by a substantial aerial campaign.
Rather than compelling Putin to sue for peace, the counter-offensive could expose Ukrainian weaknesses that embolden his ambitions. In retrospect, Washington might look longingly at the settlement terms that Ukrainian and Russian negotiators had converged upon several weeks after the Russian invasion— a Ukrainian commitment to permanent neutrality backed by a multinational security guarantee— as a missed opportunity.
Should Russia’s war of attrition threaten to force Ukraine to its knees, what would Biden do? The White House has done almost nothing to prepare the American public for a compromise settlement, let alone some form of Russian battlefield success. Having failed to lay the groundwork at home and abroad for negotiations, Biden could well face an uncomfortable choice between watching Ukraine crumble despite his promise to prevent it, and escalating U.S. or NATO involvement in ways that might produce the very military confrontation with Moscow that he has forsworn.
The American people have no right to see sensitive intelligence information, disclosure of which can certainly jeopardize U.S. national security in multiple ways. But they can and should expect that their government’s public statements do not conflict with what U.S. officials know privately from objective intelligence analysis.
Just as it did in Vietnam and Iraq, the truth about the war will eventually come out. If those painful episodes serve as a guide, it is unlikely that voters will welcome the news that they have been deceived once again in Ukraine.



 Screengrab via niacouncil.org
Screengrab via niacouncil.org Screengrab via niacouncil.org
Screengrab via niacouncil.org











