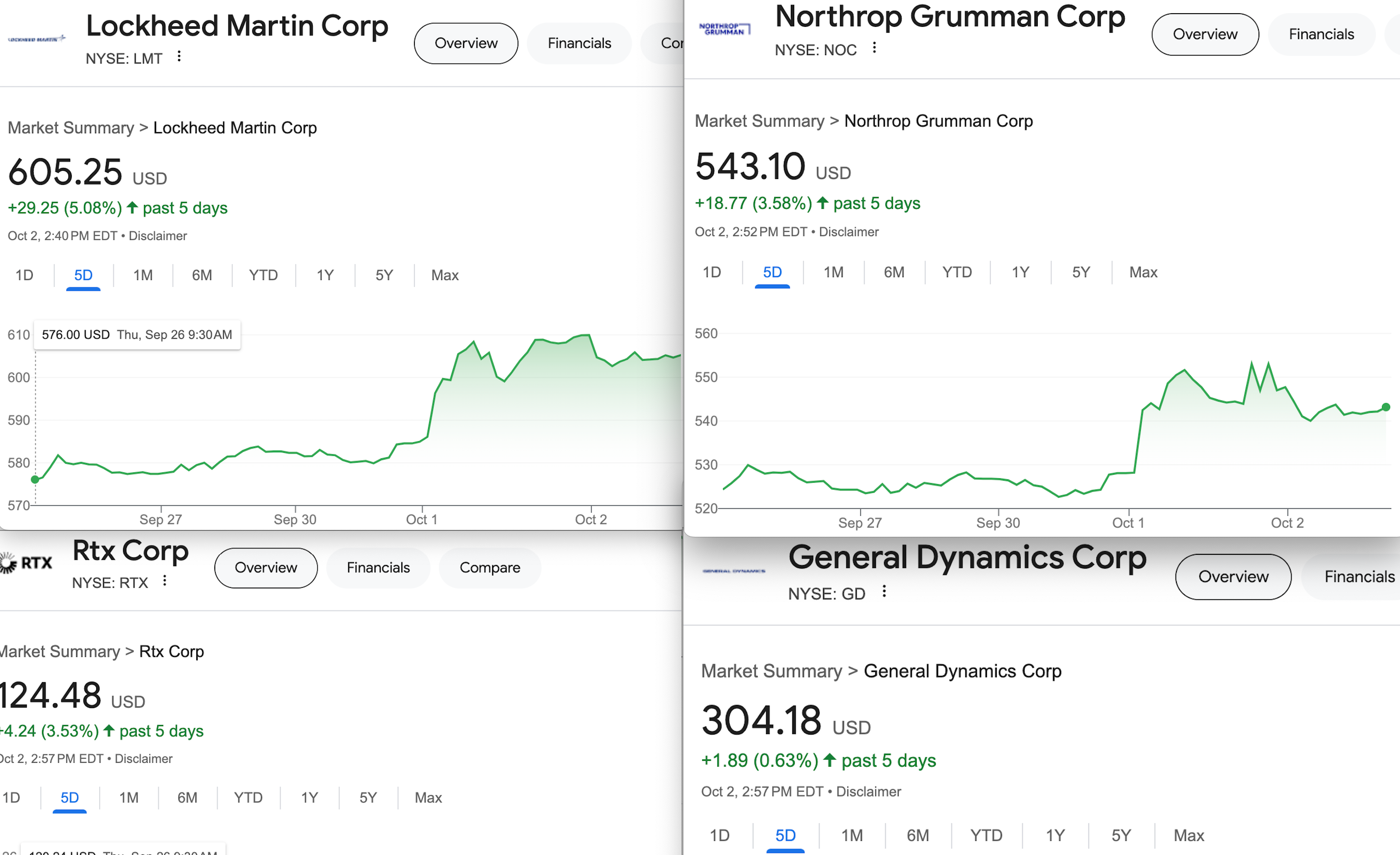
It’s a sad but familiar spectacle — as people die at the hands of U.S. weapons in a faraway war zone, the stock prices of arms makers like Raytheon and Lockheed Martin soar. A piece posted yesterday at Forbes tells the tale: “Defense Stocks Hit All-Time Highs Amidst Mideast Escalation.”
One wonders how the executives of these companies feel about their products being used for mass slaughter in Gaza and dangerous escalation in Lebanon. For the most part they’re not talking, although they are glad to occasionally inform their investors that “turbulence” and “instability” means their products will be needed in significant quantities by our “allies.”
And, not unlike the Biden administration, they tend to couch their rhetoric in terms of a “right to self-defense.” They act as if Israel’s killing of 40,000 people and displacing millions more — the vast majority of whom have absolutely nothing to do with Hamas, nor any way to influence their behavior — can somehow be white washed by calling it a defensive operation.
No one who steps outside the bankrupt world of official Washington to look at the impacts on actual human beings in Gaza, the West Bank, and Lebanon can take the notion that U.S. weapons are being used for defense in the current Middle East war seriously.
Peter Thiel and his colleagues at Palantir are an exception to the closed mouthed approach of executives at the larger weapons companies. When asked how he felt about his company’s technology to pick targets in Gaza, he said “ I'm not on top of all the details of what's going on in Israel, because my bias is to defer to Israel. It's not for us to second-guess every, everything.” And Palantir CEO Alex Karp flew the entire company board to Israel earlier this year to show solidarity with Israel’s war effort in Gaza.
At least Palantir’s leaders are honest and open about where they stand. Leaders of firms like Lockheed Martin, Raytheon, General Dynamics, and Boeing that supply the weapons that have laid waste to Gaza and are now pounding Lebanon prefer to hide behind euphemisms about promoting defense, deterrence, and stability, and assisting allies.
But what about when those allies are engaged in widespread war crimes that prompted the International Court of Justice to say that Israel’s war on Gaza could plausibly be considered a genocide? Is it morally acceptable to just cash the checks and avert one’s eyes, or do the companies profiting from this grotesque humanitarian disaster have a moral responsibility for how their products are being used?
A few years ago, during the height of Saudi Arabia’s brutal invasion of Yemen — enabled by billions of dollars of U.S.- and European-origin weapons — Amnesty International probed this very point. In a report entitled “Outsourcing Responsibility,” the group provided the findings of a survey it had done of 22 arms companies, asking them “to explain how they meet their responsibilities to respect human rights under internationally recognized standards.”
Amnesty noted that "many of the companies investigated supply arms to countries accused of committing war crimes and serious human rights violations, such as Saudi Arabia and the UAE.” None of the companies queried provided evidence that they were doing any sort of due diligence to ensure that their weapons weren’t being used to commit war crimes or human rights abuses. Fourteen companies failed to respond at all, and of the eight that did answer Amnesty’s questions gave variations on the theme of “we just do what the government allows.”
This casts influential arms makers as innocent bystanders who await government edicts before marketing their wares. In fact, weapons manufacturers spend millions year in and year out pressing for weaker human rights strictures and quicker decisionmaking on the sale of arms to foreign clients.
The weapons merchants are right about one thing. It is going to take changes in government policy to stop the obscene trafficking of weapons of war into the world’s killing zones. That will mean breaking the web of influence that ties government policy makers, corporate executives, and many members of Congress to the continued production of weapons on a mass scale. We can’t expect a profit making entity like Lockheed Martin to regulate itself when there are billions to be made fueling conflicts large and small.
Which means the responsibility for ending the killing and the war profiteering it enables falls to the rest of us, from students calling for a ban on arming Israel to union members looking to reduce their dependency on jobs in the weapons sector to anyone who wants a foreign policy driven by what makes us safe, not what makes Palantir and Lockheed Martin rich.
- Why is 'ceasefire' considered a dirty word? ›
- US sending more troops to the Middle East ›
- US is barreling toward another war in the Middle East ›
- US 'training & equipping' Lebanese Army is worst kind of déjà vu | Responsible Statecraft ›
- War drives revenue increases for world's top arms dealers | Responsible Statecraft ›
- Weapons makers cash in on Trump's Iran war ›



 Screengrab via niacouncil.org
Screengrab via niacouncil.org Screengrab via niacouncil.org
Screengrab via niacouncil.org











