The value of Lockheed Martin’s stock grew by 37 percent last year, representing an incredible financial gain for investors in the nation’s largest military contractor.
This spike was hardly the result of changing market conditions, however: the S&P 500 ended the year with growth of -20 percent. Instead, this growth came from stock buybacks. In 2022, the company bought back more of its own stock than in any other year in its history: $7.9 billion, equivalent to 12 percent of its sales income.
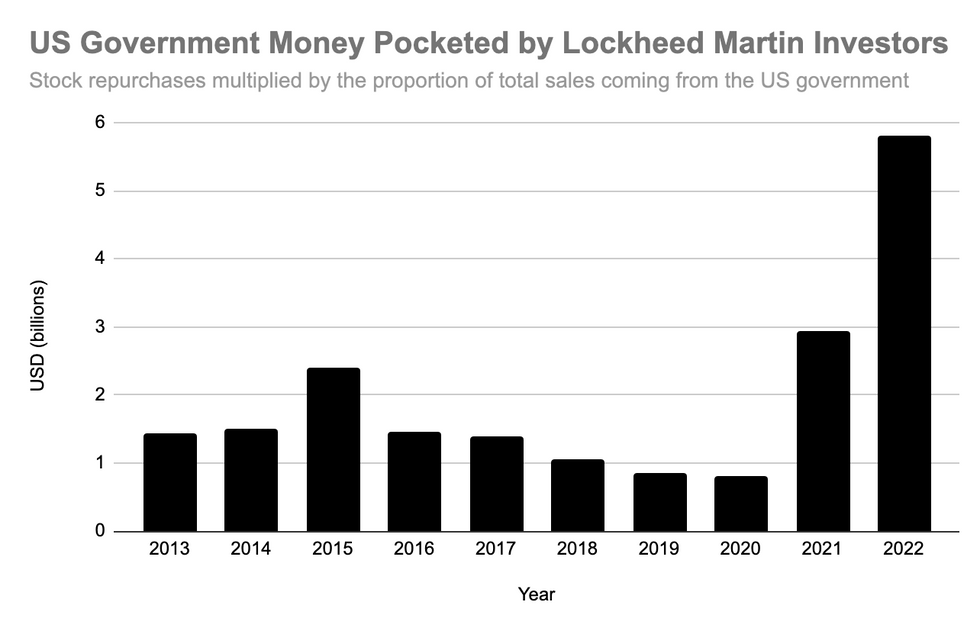
According to Lockheed’s 2022 annual report, 73.5 percent of the company’s sales last year were to the U.S. government, most of which were for the Department of Defense. In other words, if these buybacks come proportionately from the different revenue streams of the company, U.S. taxpayers underwrote $5.8 billion in Lockheed buybacks.
This is without including Foreign Military Sales, roughly another 19.2 percent of the total, which are sold to foreign governments through the U.S. government.
When contractors who receive most of their money from government sales issue buybacks, it is ultimately taxpayer dollars being redirected towards shareholders’ pockets. Data from Lockheed Martin’s annual reports suggests that company outdid itself in 2022, offering its investors a record level of taxpayer-backed buybacks equivalent to the prior four years combined.
This isn’t a new phenomenon. Since 1982, U.S. corporations have been able to buy back their own stock in order to raise the value of the remaining stock, an investor payout similar to dividends but with a smaller tax bill. The rapid growth of stock buybacks since then has attracted its fair share of critics, who argue that the money spent on them would be better used on research and development or wages, rather than enriching shareholders.
The Pentagon directs about half of its $858 billion budget to private contractors, making it a prime target for companies looking to get their hands on government cash. Indeed, Lockheed isn’t the only weapons company issuing massive stock buybacks: 2021 was a record year for the sector in this regard. But Lockheed’s latest numbers dwarf their competitors. Their 2022 buybacks were worth more than those of Raytheon, Northrop Grumman, General Dynamics, BAE Systems, and L3Harris combined.
Boeing, formerly a major spender on repurchases, suspended their buyback program in 2020 in response to scandals surrounding their commercial airliners.
Lockheed Martin has increasingly focused on buybacks to create high returns for investors over the last several years. Corporate leadership authorized $5 billion in new buybacks in the fall of 2021, and another $14 billion in the fall of 2022. The remaining funds not already spent this year are “expected to be utilized over a three-year period,” according to a Lockheed press release.
During last year’s Q4 Earnings Call, Lockheed Martin CEO Jim Taiclet bragged that the company’s buybacks and dividends “delivered approximately $11 billion to shareholders in 2022,” and that they “expect to complete our remaining repurchase authorization of $10 billion over the next few years.” Executives made it a priority “to increase cash returns to our shareholders with a significant increase to share repurchases.”
Overall, Taiclet said, the company “end[ed] the year with a total shareholder return of 40 percent.” With the majority of Lockheed’s revenue coming from the government, what Taiclet is really saying is that U.S. taxpayers helped to pay the company’s shareholders.
Bolstered by new sales related to the War in Ukraine, the company seems committed to continuing the use of buybacks. In their most recent release of financial information, Taiclet said that they “are confident in our return to growth and ability to reward our shareholders over the long run with reliable free cash flow per share expansion and cash deployment.”
The $5.8 billion share of Lockheed Martin’s buybacks enabled by government funding serves little purpose beyond further enriching investors, yet it costs more than nine times what recently-proposed cuts to food stamps would have raised each year, in their original form.
The military itself has raised alarms about its contractors’ use of buybacks. A report from the Pentagon earlier this year found that, when comparing the 2010s to the 2000s, “defense contractors chose to reduce the overall share of revenue spent on [Independent Research & Development] and Capital Expenditures… while significantly increasing the share of revenue paid to shareholders in cash dividends and share buybacks by 73 percent.”
These problems have not gone unnoticed. Sen. Elizabeth Warren (D-MA) has been particularly vocal about the harmful implications of these trends. “As major defense contractors brag to their shareholders about increasing dividends and buybacks, they can’t expect taxpayers to further underwrite their profits.” But until reforms are made which limit buybacks or reform the contracting process, the companies involved will continue to expect exactly that.
Lockheed Martin did not respond to a request by RS for comment for this story.