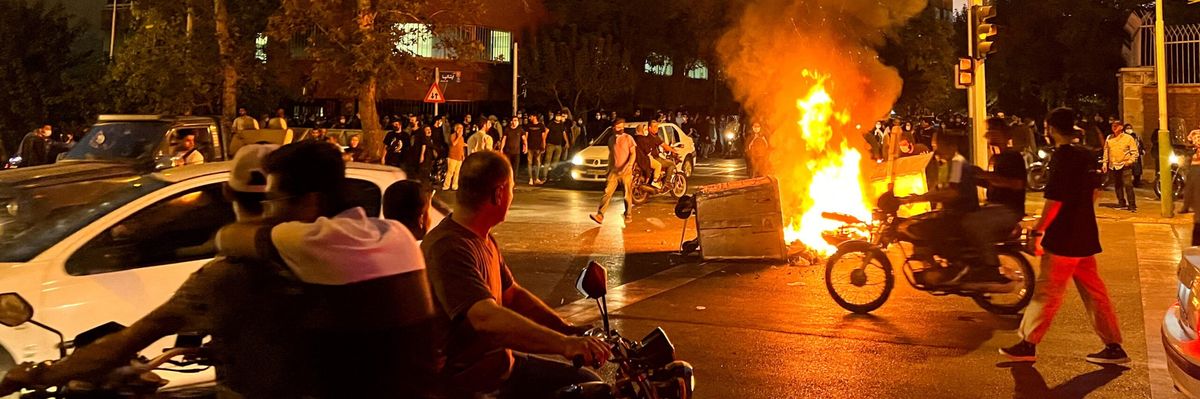Since at least 2009 and the “Green Revolution,” the young and middle-class population of Iran has repeatedly demonstrated its disgust with the aging clerical rulers who govern their lives. They march in the streets at risk of everything to denounce the brutal and inflexible dictatorship that abuses the revolutionary power given to them by the people in 1979.
In each instance, as the scope of the demonstrations expand and the slogans become ever more incendiary, observers inside and outside Iran ask themselves if this is a new revolution. In every case to date, the truncheons of the security forces have proved more powerful and enduring than the spirit of the demonstrators. Like it or not, this untrammeled use of organized force against brave but disorganized demonstrators is likely to prevail in the current set of headscarf riots.
Given the undeniable opposition of a large and growing proportion of the Iranian population to the existing sclerotic theocratic state, it is legitimate to ask when and how this simmering discontent may be transformed into political change.
One way to think about this unknowable outcome is to look at the last time such a movement was successful in Iran — specifically the Iranian revolution of 1979 itself. There were two essential characteristics of Khomeini’s revolution: First, it was unarguably authentic, emerging from the political-minded Iranian clergy in Qom and Najaf, not subject to the influence of any outside power.
Second, it benefited from more than a decade of structural organization that used the mosque as a decentralized center for meetings, planning, fundraising, and mobilization — a highly public yet covert “home” where the revolution acquired heft and policy substance over several decades.
Leadership was, of course, important, especially in the final stages of the revolt. But I would argue that leadership without the underlying structural foundation would merely have provided the Shah with an irresistible target.
So, what happens if we apply the two criteria above to the present circumstances? The short answer is that things have become far more difficult for any would-be revolutionaries. The old men who made the revolution of 1979 learned their lessons well. The Shah, for all his reputation, never seemed to believe that Iranian clerics were capable of mounting a major challenge to his regime.
According to Richard Helms, who had previously served as CIA director and U.S. ambassador to Tehran, the Shah’s first question to him when he came to visit at New York hospital in late 1979 was to the effect: Why did you do this to me? He continued to believe that either the CIA or the Soviets made it happen. This was a huge advantage to the folks planning the revolt from their scattered mosques. The Shah was given by SAVAK, his secret police, a list of the revolutionary ringleaders, but he refused to round them up. The explanation for this seems to lie in the Shah’s own peculiar sense of kingship and his mystical relationship to his people. But whatever the rationale, the Shah’s enemies, who are now running the country, will never make that mistake.
Today, the aging revolutionaries around Khamenei spend a great deal of time and effort watching for any signs of political opposition and intervening proactively to nip it in the bud. They arrest anyone showing any signs of leadership, interrogate and hold them for prolonged periods, and then frequently release them with the understanding that they will utter not a word about politics or else pay a much higher price. The most dangerous are confined to permanent house arrest. It works.
So the growth of an authentic anti-regime political movement is far more difficult today than it was during the 1979 revolution. Needless to say, the mosque as a home for such incipient movements is no longer available since it has become an institution of the state.
Does this mean that a revolt is impossible? Absolutely not. The times are different, the circumstances have changed, but when people know they are fighting for their personal and national liberty, there will be those brave and bold enough to find a different path.
I would wager that there are secret meetings going on today, on the fringes of the demonstrations and under the noses of the Revolutionary Guards. We have no way to know this, and the chances are that, if these covert efforts to build an authentic anti-establishment movement succeed in eventually producing results, we — the West and the rest — will probably be the last to know.
The possibility of still another intelligence failure on the order of 1979 is far from impossible. But we should welcome that: the urge to meddle and to “guide” the opposition is probably irresistible in Washington and elsewhere. But a Western fingerprint on any opposition movement is likely to be a kiss of death.
One thing the United States and others can do to improve the odds is make available a virtual home to future revolutionists. A few steps have been taken to permit Western sales of tech equipment that can bypass the fine-grained surveillance of the Iranian security forces, but this is a spigot that should be opened as wide as possible. If the tools of revolt are available over the counter, the Iranian opposition will figure out how to use them, just as their predecessors mastered the use of the humble cassette tape to send words of policy and encouragement to a wide audience inside Iran. U.S. sanctions policy should be given a good scrubbing so we do not inadvertently keep shooting ourselves in the foot.
But, above all, we should be modest in our expectations. The Iranian revolution, it can be argued, began its initial stages in 1963 — fifteen years before the revolution — when Khomeini was exiled to Iraq. By that yardstick, patience should be the name of the game. At a minimum, we should exercise utmost care that our policies toward Iran provide the necessary breathing space for a movement that Iranians themselves must create under the most difficult circumstances possible.