The Biden administration’s upcoming Summit of Democracy sets out a noble goal: bringing together democratic governments to defend against authoritarianism, address and fight corruption, and promote respect for human rights. Coming after President Trump spent four years overtly courting authoritarians and undermining America’s democratic institutions — culminating in a riot targeting the peaceful transfer of power — President Biden clearly hopes that the Summit can restore American leadership and start to buck the trend of illiberal and oligarchic authoritarianism that has spread across the globe and found roots in the Republican Party.
However, to be a meaningful rather than a self-congratulatory exercise will require the Biden administration — and the foreign policy establishment writ large — to ask some hard questions. At the top of the list should be why the United States actively supports so many authoritarian governments while imposing crushing sanctions on many of the rest.
As Matthew Hoh of the Center for International Policy pointed out, the United States supports 74 percent of the non-democratic nations of the world militarily. Most of the rest of the non-democratic nations are subject to punishing sanctions. This combination is effectively a one-two punch to civil society, human rights, and democratic movements.
To most, it is self-evident that backing dictators like the Saudi monarchy or Abdel Fattah el-Sisi in Egypt with weapons and money is the antithesis of supporting democracy. But far fewer recognize that sanctions also work to entrench authoritarian governance and fuel corruption, increasing the power of the state at the expense of civil society.
The academic literature around the impact of comprehensive sanctions is quite clear. Authoritarian governments typically do not fold in the face of economic coercion, and in many cases their hold on power is consolidated. As academics Dursen Peksen and Cooper Drury wrote, authoritarian governments targeted by sanctions “can intervene in the market to control the flow of goods and services made scarce by foreign economic pressure,” allowing the leadership to “redirect wealth toward its ruling coalition and away from its opponents to minimize the cost of sanctions on its capacity to rule.”
Similarly, while democratization is a complex phenomena, a strong middle class and economic prosperity have typically been major drivers of successful democratic movements. However, the middle class of sanctioned societies often bears the largest brunt of far-reaching sanctions. As economic pain increases, organizers are forced to take on more work to support people’s basic needs like food and healthcare.
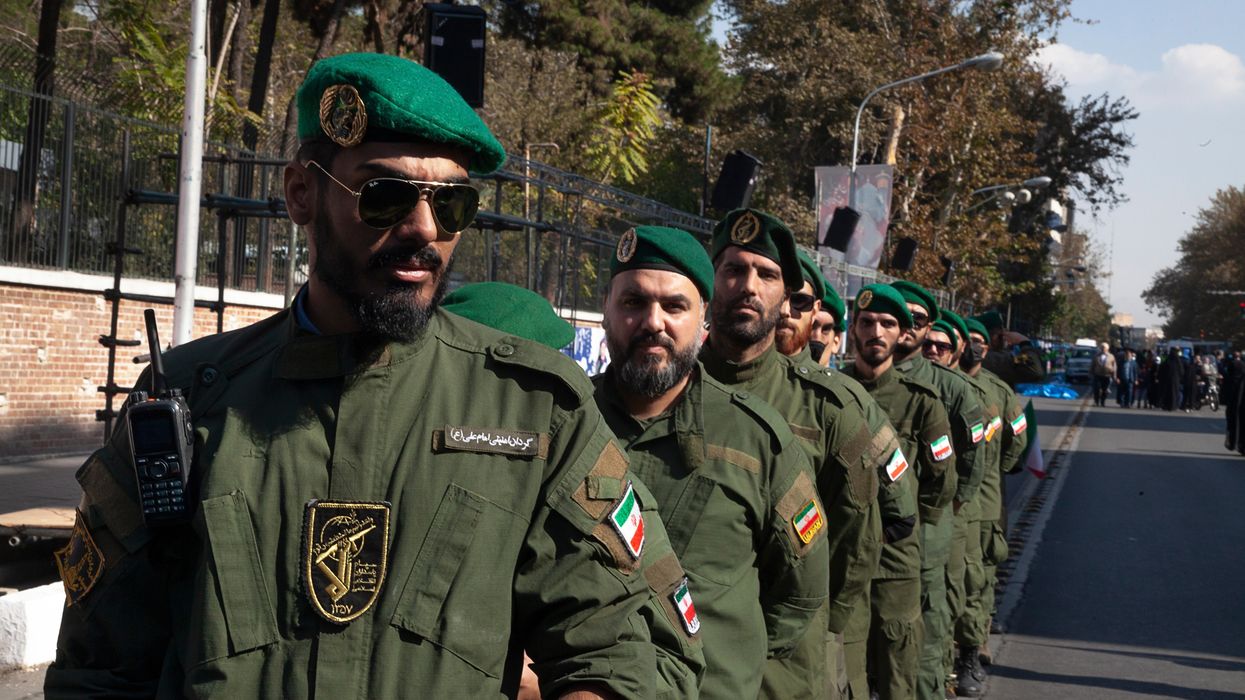
Iran has been a clear example of the negative impacts of sanctions on civil society. Despite widespread disaffection with the government, the return of crushing sanctions has spread immiseration while empowering Iran's most illiberal and anti-democratic forces. According to Djavad Salehi-Esfahani, between 2011 when financial sanctions were significantly escalated by the Obama administration and late 2020, more than 8 million Iranians fell from the middle class to the lower-middle class while 4 million more fell into poverty. Similarly, hyperinflation driven by sanctions has dramatically increased the cost of living, with 40 percent of Iranians struggling to eat enough food. As Azadeh Moaveni and Sussan Tahmasebi warned earlier this year, “middle-class women have seen their lives and hopes crushed by the Trump administration’s sanctions,” with the net result being that the “‘middle-class woman’ in Iran is a disappearing category.”
As crushing sanctions have dealt a painful blow to civil society, the Islamic Revolutionary Guard Corps has taken on a larger role in smuggling and sanctions busting. Thus, a repressive and hardline-dominated institution has gained at the expense of ordinary citizens. While the people of Iran are furious at their circumstances, conservatives and hardliners have solidified their control over all national governmental institutions with little counterweight.
Rather than perpetuate a status quo that spreads misery and bolsters authoritarianism, Washington could instead support civil society by easing far-reaching sanctions regimes like those leveled against Iran. In the case of Iran, doing so would ease inflationary impacts on the Iranian economy that would allow more Iranians to put food on the table and rejoin the middle class. This, in turn, would allow for many more Iranians to focus on organizing around political demands instead of for basic survival.
The U.S. approach to the world shouldn’t swing wildly between blind support for certain authoritarian governments and unrelenting sanctions on others. The United States should be able to engage both the kingdom of Saudi Arabia and the theocracy in Iran — as well as other governments — to hold them accountable and seek to affect their behavior without undermining civil society or liberal values.
With the Summit for Democracy approaching, serious self reflection is needed. Not only is the United States under serious risk of democratic backsliding due to threats from within, but it must carefully balance competition with coordination to address some of the biggest threats of our time, like climate change. However, even an honest conversation risks missing how U.S. foreign policy has sustained, rather than undermined, authoritarian governance across the globe. As a result, the deleterious impact of U.S. sanctions and military assistance must be on the table.