After eight months of failing to treat the war, atrocities, and famine in the Tigray region of Ethiopia with the seriousness that they deserve, the United Nations Security Council is finally meeting on the crisis as early as this week. What has occasioned this is the military triumph of the Tigray Defense Force over the Ethiopian army.
For the resolution of the crisis — indeed, for the very survival of Ethiopia — the Security Council must deal directly with the TDF, which is the armed wing of the former ruling party, the Tigray People’s Liberation Front, or TPLF.
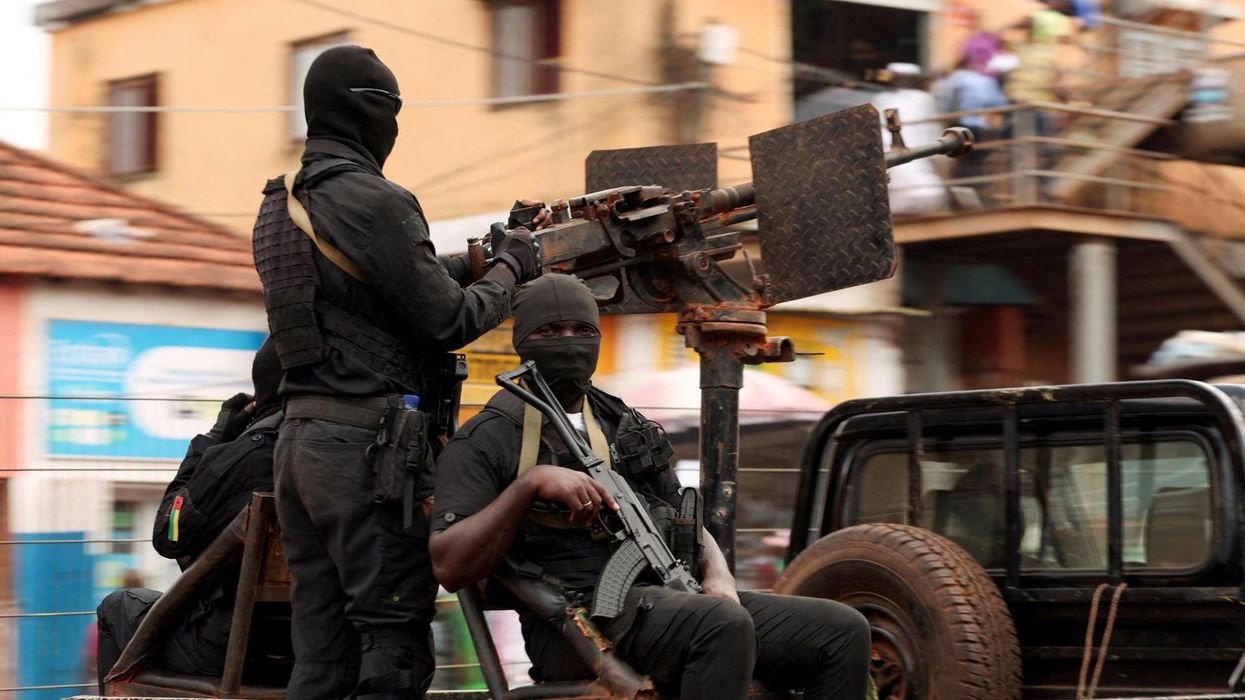
In two weeks of fierce fighting in June, the TDF defeated the Ethiopian army, with a decisiveness and speed that surprised even its own commanders. Driven by a fierce determination to free its land from the brutalities of occupation, led by veterans with surpassing military skill, and now armed with its enemies’ weapons, the TDF inflicted irreparable losses on the Ethiopian National Defense Force. The Tigrayan resistance captured or put out of action more than half of the Ethiopian army’s combat capabilities. The Eritrean army — the Ethiopians’ formidable ally — is withdrawing its units from the town it occupied in northern Tigray, and the regional militia of Amhara that overran western and southern Tigray may well flee rather than fight.
Focused on the human rights atrocities and the humanitarian disaster in Tigray, the media and diplomats entirely missed the story of the war itself. Everyone knew that the official line of the government in Addis Ababa — that a “law enforcement operation” needed just a bit more effort to round up the “remnants” of the former TPLF — wasn’t true. But few understood quite how strong the armed resistance was growing.
The number one reason why the guerrillas were so numerous, determined, disciplined, and bold was that their sisters and daughters had been raped, their farms and houses had been burned, and they themselves faced torture and murder if caught by the occupiers.
Ethiopian Prime Minister Abiy Ahmed and his coalition partner, Eritrean President Isaias Afewerki, seemed to believe they could grind the Tigrayan populace into submission by sheer cruelty. Rarely can a policy of war crimes — the Tigrayans call it genocide — have backfired so spectacularly. The Tigrayans had nothing to lose and fought for their lives.
Among those who took up arms were people who didn’t support the TPLF, but rallied to the fight for survival.
That was Abiy Ahmed’s first folly. He also over-estimated his military skills and believed in his own propaganda, apparently thinking that one more push would finish the job. After the TDF had annihilated five full army divisions on June 22, Abiy ordered three more divisions into the same trap. They met the same fate. In numerical terms, the Ethiopian army has lost about half its forces; in fighting capacity, it is destroyed.
After their remaining brigades fled from the Tigrayan capital Mekelle, the Ethiopian foreign ministry announced a ceasefire. This would be comic were it not so tragic. Ethiopia doesn’t have any troops in Tigray who can fire any shots. Most of the statement is instructing imaginary government departments to carry out activities in places where they have no presence. The announcement had a sinister ring because it said that the ceasefire was to allow farmers to cultivate — indicating that when the farming season is over in three months’ time, the ceasefire will lapse. Abiy’s ministers are on an arms-shopping spree and have said they intend to reoccupy Tigray at that time.
The TPLF rejected the ceasefire. Spokesman Getachew Reda said their forces would pursue their enemies and make sure they can’t pose any future threat to Tigray.
Nonetheless, UN Secretary General Antonio Guterres and African Union Chairperson Moussa Faki welcomed Abiy's ceasefire statement. The most charitable explanation is that they still believe — contrary to all evidence — that Abiy can be persuaded to act rationally. Neither the U.N. nor the AU considered how their statements might be received by Tigrayans. That’s a dangerous oversight.
The United States also cautiously accepted the ceasefire statement as a possible first step. A State Department statement laid out what was needed to make it real, including humanitarian access, verified withdrawal of Eritrea, investigations of war crimes, and political dialogue. That’s a good list, and it should form the U.N. Security Council agenda.
A humanitarian ceasefire needs to specify how the government will permit aid operations to reach the TDF-controlled areas, which have a population of more than five million people who need emergency aid. The only way to get food and medicine to them — and seeds and tools to farmers — is along roads controlled by Ethiopia and Eritrea, or through Ethiopian airspace. Aid workers need Ethiopian government permits to go to Tigray. Just last week, Abiy gave an interview in which he accused aid agencies of conspiring to overthrow the government. The next day, three staff members with Doctors without Borders were murdered by unidentified assailants. For good measure, Abiy also denied there was hunger in Tigray. And on June 30 the prime minister held a press conference and made it clear that his goal was to encircle and starve Tigray.
The key element in the withdrawal of Eritrean and Amhara forces is that it should be verified. That means international observers on the ground. Given that Reda’s threat to counter-attack across the border is real, it also means a guarantee on the security of the border, to protect both sides.
Also key is an explicit ban on hostile military flights. Last week a market town was bombed, killing scores. If that happens again, the TDF would likely retaliate.
A ceasefire should include third-party monitoring and a mechanism for reporting and investigating complaints. Another issue is prisoners of war — the TDF has at least 10,000, while the federal government detained more than 12,000 Tigrayan officers at the outbreak of the war.
Most important, a ceasefire should be a step towards political negotiations aiming for peace. Often, a ceasefire agreement includes a commitment to ending hostile rhetoric. That isn’t happening. The Ethiopian statement indicates the opposite intent. It refers to the Tigrayan political leaders as “the criminal clique.” Reda routinely describes the government as “fascist.”
Popular sentiment in Tigray favors secession: people argue that if Ethiopia doesn’t want them, then they should set up their own state. Abiy’s hostile rhetoric, and efforts to impose a blockade on essential aid, might well push the TPLF to declare independence.
Most observers believe that if Tigray tries to secede then Ethiopia will disintegrate, following the path of Yugoslavia towards multiple ethnic wars. The Tigrayan leadership has said that it does not want to be the one that sets this process in train. But Abiy’s bellicosity might just make that decision inescapable.
The international community doesn’t have much leverage with the Tigrayans. It hasn’t given them any material assistance. It has hardly even spoken to them — until today, diplomats rely on Tigrayan leaders calling out on unsecure satellite phones, and there’s no way of sending documents. That needs to be remedied at once.
The United Nations should send a high-level envoy to Mekelle to meet with the Tigrayan leadership and listen to their demands. The world needs to do business with the TPLF/TDF. Not just Tigray but Ethiopia depends on them.