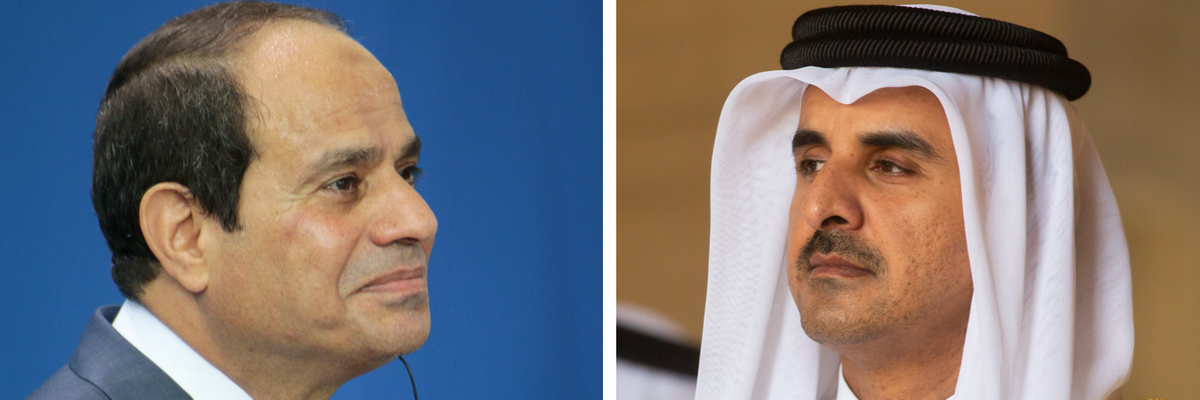
The resumption of diplomatic relations between Egypt and Qatar, announced January 20, marks an important step toward easing tensions within the Arab world exacerbated by the Emirati- and Saudi-led blockade of Doha that began in mid-2017. The two countries’ official rapprochement could also add to pressure on the al-Ula accord’s other signatories — particularly the United Arab Emirates (UAE) and Bahrain — to follow Cairo’s lead and move past the three-and-a-half-year-old Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) crisis.
Between the January 5 al-Ula summit and the official resumption of bilateral ties, Egypt and Qatar’s relationship began moving in a very positive direction. In the immediate aftermath of the unity accord’s signing in Saudi Arabia, Qatari Diar Real Estate Company (a company owned by Qatar’s sovereign wealth fund) held its opening ceremony for its wholly-owned St. Regis Hotel in Cairo. Alongside U.S. Treasury Secretary Steven Mnuchin, Qatar’s Finance Minister, Ali Al Emadi, participated in the ribbon-cutting, marking the first visit to Egypt by a senior Qatari official since the GCC crisis in mid-2017.
As Emadi put it, “This project represents a new addition to the Qatari investments in Egypt, exceeding five billion dollars in various fields.” His Egyptian counterpart, Mohamed Moait, responded by congratulating Qatari Diar for “the inauguration of this pioneering hotel, which is a result of the company’s decision to invest in the tourism sector, one of the most important sectors for Egyptian economy.” Thirteen days later came the first direct flight between Qatar and Egypt since 2017.
It is difficult to see this thaw in Egyptian-Qatari relations as unconnected to the advent of the Biden presidency. The leadership in Cairo, much like the Al Saud rulers in Riyadh, has serious concerns about the new administration’s intentions. Egyptian officials remember very well that the Obama administration, in which Biden served as vice president, halted some arms sales to Egypt as punishment for the regime’s crackdown following the 2013 coup. They now worry that new administration will similarly push Egypt on human rights-related issues. By restoring diplomatic ties with Doha, Egypt will have presumably bought some goodwill with Washington, which, even under Trump, saw the blockade as harmful to U.S. interests.
But the transition in Washington is not the only factor behind the Egyptian-Qatari rapprochement. Cairo’s perception of Qatar and its backing for Islamist parties in the Arab world as a threat has steadily decreased in recent years. “The Egyptians have realized that Qatar has become quiet over the last seven years. It’s in no way a threat that they made it out to be seven years ago,” Andreas Krieg, a lecturer at the School of Security Studies at King’s College London, told Responsible Statecraft. “In this respect, there aren’t any real grievances anymore from the Egyptian side. The only real grievance that remains for the Egyptians is [cable news channel] Al Jazeera. But even Al Jazeera in recent years hasn’t really singled out Egypt in its coverage.”
According to Krieg, Abdel Fatah al-Sisi’s regime is in a far more secure position today compared to the time when it came to power after toppling Mohammed Morsi’s government in 2013 or even when the Gulf crisis erupted in 2017. Despite the persistent view among Cairo’s officials that the Muslim Brotherhood poses their greatest threat, the fact that most of the Islamist movement’s Egyptian members have moved out of Qatar to Turkey makes it easier for Cairo to reconcile with Doha. Today, Egyptian policymakers “don’t see any strategic value for themselves in playing the role of the thorn to keep the Qataris on their toes,” Cinzia Bianco of the European Council on Foreign Relations told Responsible Statecraft.
Cairo also sees financial advantages to normalizing ties. In addition to a renewed fount of foreign investment, the roughly 300,000 Egyptians who work in Qatar, whose remittances to families back home are an important source of hard currency, should gain more confidence and stability in the tiny Gulf state. They will no longer have to depend on Greece’s embassy for whatever consular assistance they may require.
Understanding Egypt’s new position on Qatar also requires taking stock of the important role that Saudi Arabia plays in Cairo’s foreign policy decision making. As Saudi Arabia has most recently been the most eager over the past year of the anti-Doha Quartet to mend the rift with Qatar, Egypt’s decision to reconcile with Doha offers a way to support Riyadh as the GCC’s historic and continuing regional heavyweight. Bahrain, on the other hand, has shown a greater reluctance, suggesting a closer alignment with UAE, the most enthusiastic of the four blockaders.
Despite the very recent positive developments in Egyptian-Qatari ties, the relationship will probably be at best a “cold peace” due to a number of issues that have fueled tensions between them.
Libya’s civil war, where the two countries find themselves on opposite sides, is probably the most sensitive file. Doha closely aligned itself with Turkey in support of the internationally recognized Government of National Accord (GNA), while the Egyptians, along with the UAE, have backed the Tobruk-based Libyan National Army headed by Field Marshal Khalifa Belqasim Haftar. Cairo fears that Islamist groups in the GNA will consolidate their position in a country that shares a long and porous border with Egypt. In the absence of diplomatic progress toward ending that conflict, the war will remain a sore point between Doha, which has long favored treating Islamist parties as legitimate political actors in the Arab world, and Cairo, which sees them as terrorists.
Beyond Libya there are other regional dossiers, from Sudan’s ongoing political transition, to growing Qatari influence in South Sudan, to Hamas in Gaza – to which Doha has provided, with Israel’s acquiescence, critical financial support -- that will likely continue to irritate Egyptian-Qatari relations. As Cairo has high stakes in the outcome of the Grand Ethiopian Renaissance Dam (GERD) dispute, cooperation with both Sudans is critical to Egypt’s efforts to secure its national interests vis-à-vis East Africa while tensions between Egypt and Ethiopia remain hot. Cairo will most likely not welcome Qatar pursuing its ambitions in this tense region. Just as Cairo saw Qatari support for Islamist factions in Sudan as a direct threat to Egypt during the Hosni Mubarak era, Sisi’s regime could easily be unsettled by Doha possibly regaining influence in Khartoum (which significantly faded after President Omar al-Bashir’s 2019 ouster) or making further inroads in Juba despite this month’s official Egyptian-Qatari rapprochement.
As the largest Arab country with a population of 106 million, Egypt is making a bold move that bodes well for creating badly needed space for dialogue in a region beset by conflict and ideological polarization. To be sure, Egypt and Qatar’s relationship will continue to have difficulties. The mistrust that has built up since 2013 will not evaporate quickly. But to Cairo’s credit, it has recognized the value of diplomacy over confrontation in dealing with its concerns about Qatar’s regional policies.