The United States is bombing Yemen, and according to the news coverage the reason is a string of recent attacks by Houthi militants on commercial ships in the Gulf of Aden. A New York Times headline from last week is typical: “After Red Sea Barrage by Houthis, U.S. and Allies Weigh Retaliation.”
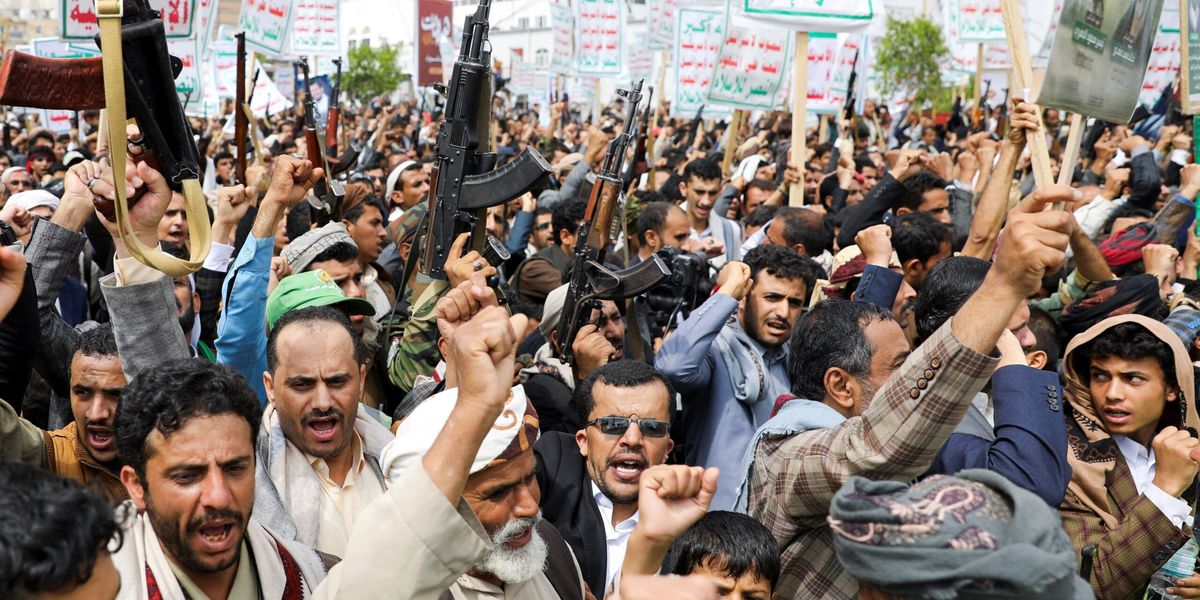
This is technically true. Since November, the Houthis, who receive weapons and aid from Iran, have launched dozens of missiles at vessels in international shipping lanes, leading some ships to avoid the Red Sea entirely and sail all the way around Africa. But contra the headlines, the Houthis didn’t suddenly become aggressive last year nor did American meddling in Yemen begin yesterday.
The U.S. has been trying to dislodge the Houthis for almost a decade now. It’s failed, and there’s little reason to think the current effort will succeed either.
American involvement in Yemen began in 2015 after the Houthis invaded and captured the Yemeni capital of Sanaa. In response, Yemen’s neighbor Saudi Arabia assembled a coalition of Arab nations and began bombing Houthi targets, with the U.S. providing arms, logistical support, and other assistance like midair refueling for Saudi jets. It was seen as reluctant realpolitik on Washington’s part: The Saudis felt cold-shouldered by the West’s nuclear deal with their hated rival Iran, so the Obama administration reassured them by backing their war.
From the beginning, Yemen’s conflict was a strange fit for American involvement. At stake were largely local issues: The Houthis were Zaydi Muslims, an idiosyncratic sect of Shiite Islam, who had historically complained of discrimination. They were allied with a former president of Yemen who was trying to depose a then-current president of Yemen. There was also a sectarian overlay: The Houthis were Shias backed by Iran while the Saudis and its allies were Sunnis.
You’d think Washington would have learned from the failure of the Iraq war to stay out of Islamic sectarian battles. If the United States had any interests in Yemen at all, it was in keeping a Sunni group and an enemy of the Houthis, al-Qaeda in the Arabian Peninsula (AQAP), at bay. Instead as the Saudis further destabilized Yemen, into the chaos stepped AQAP. They fanned out across the eastern part of the country, establishing a foothold as never before, with many analysts suggesting they were the most dangerous al-Qaeda franchise on Earth.
Here was another lesson from Iraq: Instability is a terrorist’s best friend. The Houthis in a sense were an echo of Iraq too. As Bruce Riedel has written, “The American invasion of Iraq in 2003 deeply radicalized the Houthi movement, like it did many other Arabs. …It was a turning point largely unrecognized outside Yemen, another unanticipated consequence of George Bush’s Iraq adventures.” Now, the American intervention in Yemen was yielding horrific civilian casualties and humanitarian strife, driving locals into the arms of both al-Qaeda and the Houthis, the very groups we were trying to stop.
This is the Yemen into which America is hurling fresh ordnance today, one emaciated by war and bloodshed. It’s the poorest country in the Middle East. The U.N. says it’s home to the world’s worst humanitarian crisis. The Houthis have survived the Saudi coalition and are increasingly confident they can outlast any challenger. The American-recognized Yemeni government is still banished from Sanaa and holed up in the country’s south.
Meanwhile the United States is once again finding that dislodging the Houthis is more complicated than it seems. Dropping bombs is easy; influencing events on the ground less so. So it was that, as the New York Times reports, while recent U.S. airstrikes in Yemen “damaged or destroyed about 90 percent of the targets struck, [Houthi forces] retained about three-quarters of its ability to fire missiles and drones at ships transiting the Red Sea.” The Houthis have since vowed to retaliate against the U.S. while Sanaa recently hosted a large anti-American rally.
It’s a pattern that’s played out time and again: The U.S. intervenes somewhere; this empowers our putative enemies who take advantage of the chaos and win hearts and minds; those enemies launch an attack; the U.S. uses the attack as a pretext for another military action; rinse and repeat sans any historical memory. Remember this the next time you hear that our hand was forced by the Houthis.
- Yemen’s drone doom loop: A model of instability for fragile states ›
- Dem, GOP Lawmakers say Biden had no authority to launch Yemen strikes ›
- US strikes on Yemen won't solve anything ›
- Gulf states wary of US-led strikes on Houthis | Responsible Statecraft ›
- The enduring problem with proxies | Responsible Statecraft ›