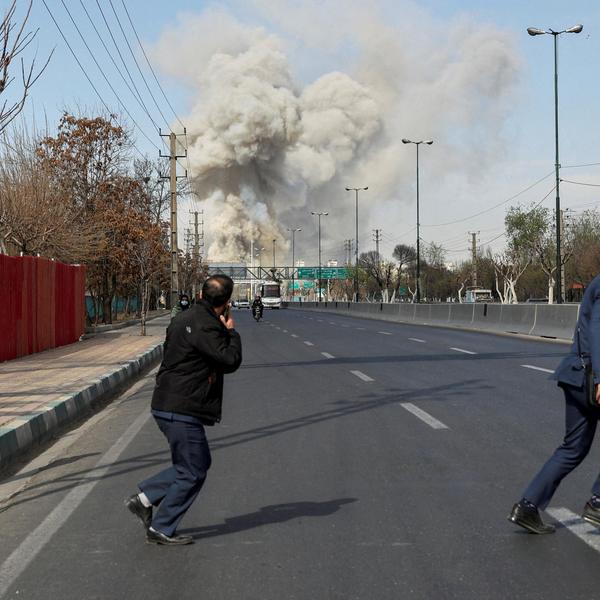
When it was reported this week that former President Joe Biden’s FBI may have targeted the cellphones of eight Republican senators in the "Arctic Frost” investigation related to the January 6, 2021 Capitol Hill riot, the Republicans that were supposedly surveilled were not happy about it.
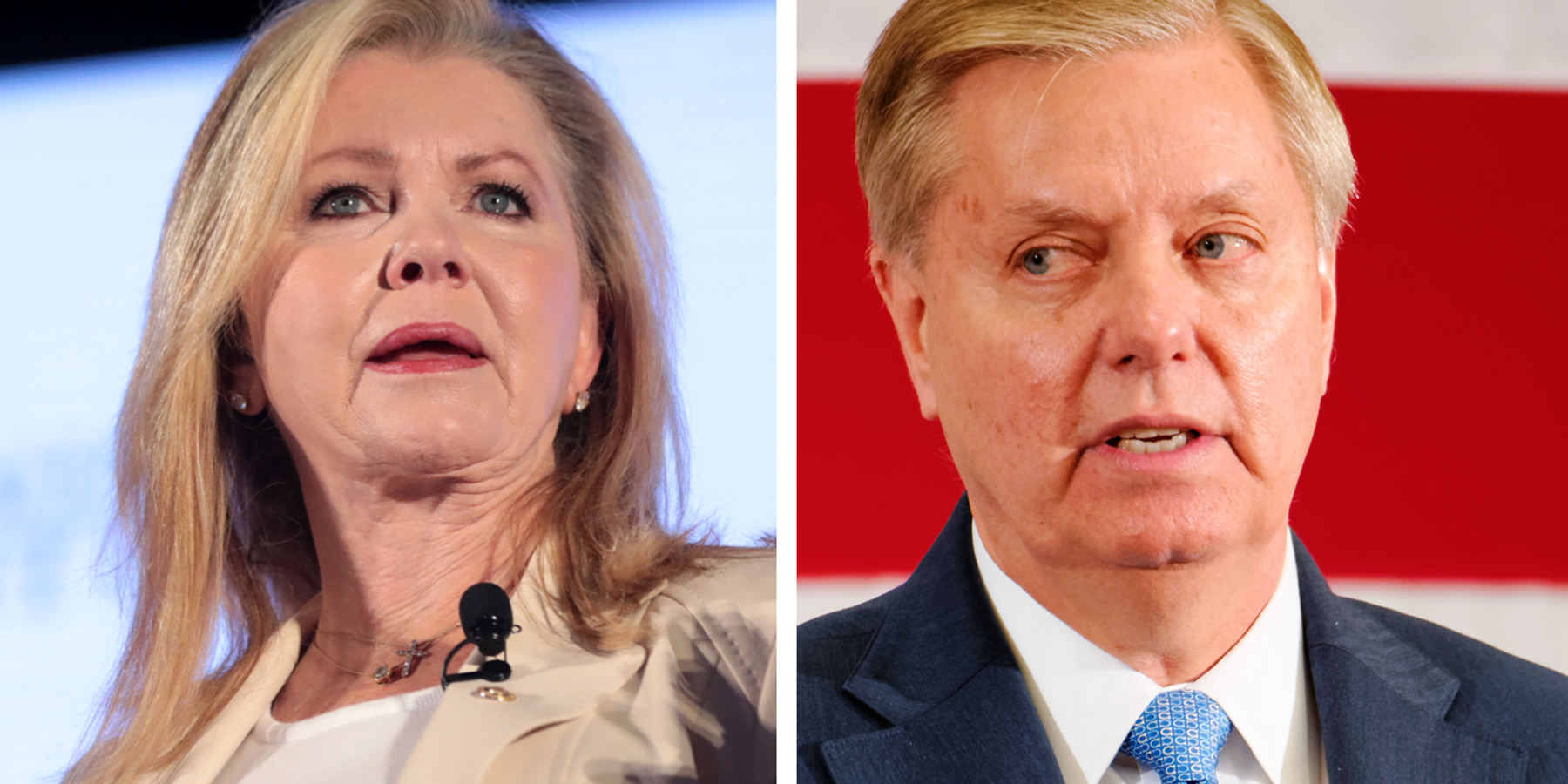
One was Sen. Marsha Blackburn (R-Tenn.), who posted on X Wednesday, “We need to know why (ATT) and (Verizon) did not challenge the subpoena for the phone records of eight United States senators when the Biden FBI spied on us during an anti-Trump probe.”
“There needs to be a reckoning for this,” she declared.
On Thursday, Republican Congressman Thomas Massie (R-Ky.) explained to Blackburn why this might have happened, “It’s called the Patriot Act, FISA, and CISA.”
“Please vote no next time,” he insisted.
During her tenure in the House, Blackburn voted for the Patriot Act each time it came up for renewal since it was passed in 2001 and numerous other federal surveillance measures since that time too.
The Patriot Act was first hastily signed into law in the politically charged days and weeks after 9/11, significantly expanding the federal government’s spying and law enforcement powers. Section 215 allows the F.B.I. to obtain secret court orders and to collect any business records the agency deems vital to national security.
This Act supposedly designed to target potential terrorists has since been used to go after drug dealers, track website users, parents at school board meetings, and more.
Perhaps even spying on Republican senators.
Senator Lindsey Graham (R-S.C.) has long been a vocal champion of the Patriot Act. He was also one of the Republicans reportedly surveilled — and he’s very mad about it.
In a Senate Judiciary Committee hearing on Tuesday, Graham roared to Attorney General Pam Bondi, “Can you tell me why my phone records were sought by the Jack Smith agents?” — Smith being the J6 investigation special counsel.
“Why did they ask to know who I called and what I was doing from January 4th to the 7th?” Graham wondered loudly and aggressively.
In May 2015, after Sen. Rand Paul (R-Ky.) attempted to block an extension of the Patriot Act with a ten-plus hour filibuster, Sen. Graham famously rolled his eyes over Paul’s efforts.
Paul warned that the Patriot Act undermined civil liberties. Then and now, Graham has always appeared to have full faith in the government handling power responsibly.
Now Sen. Graham seems shocked — shocked — that the FBI might have intruded so easily into his own privacy.
There is little doubt that Sens. Blackburn or Graham are genuinely outraged that they may have been spied on, and it probably feels personal.
But there is something to be said about these Republicans’ privacy possibly being breached through government tools they championed.
Because they can’t say they weren’t told.
Sen. Paul, like Rep. Massie, and Congressman Ron Paul before them, and a handful of other libertarian-leaning Washington lawmakers have long warned that giving intelligence officials unconstitutional or at least extra-constitutional powers was a threat to Americans’ basic privacy.
A handful of progressives, like Independent Sen. Bernie Sanders and former Democratic members of Congress like Dennis Kucinich and Cynthia McKinney in the past have consistently opposed the Patriot Act on similar grounds.
In fact, the only Senator to vote against the Patriot Act at its inception in October 2001 was Democrat Russ Feingold.
When Republican Ron Johnson ran against Feingold in 2010 and defeated him to win that Wisconsin senate seat, Feingold touted his lone opposition to the Patriot Act in ads throughout his campaign, while Johnson dismissed his opponent on that front.
Sen. Johnson has been a supporter of the Patriot Act. He was also one of the GOP senators allegedly spied on.
Johnson posted on X on Tuesday, “By now, it should be obvious that partisan leftists are the danger to our democracy. The latest example: Biden’s FBI went on a fishing expedition and subpoenaed the phone records of 9 members of Congress.”
“This should shock and outrage every American,” he contended. It should. For some, it long has. For at least these three Republican senators, this never shocked them until this week.
When a then-still unknown Edward Snowden revealed in 2013 that the NSA had been collecting the phone data of millions of Americans, Sen. Graham said he was “glad.” “I’m glad the NSA is trying to find out what the terrorists are up to overseas and in our country,” Graham responded.
Perhaps the Biden administration was glad to see what Lindsey Graham and his Republican friends might have been up to too.
- Former NSA chief revolves through OpenAI's door ›
- 9/11 militarized law enforcement and made every American a suspect ›