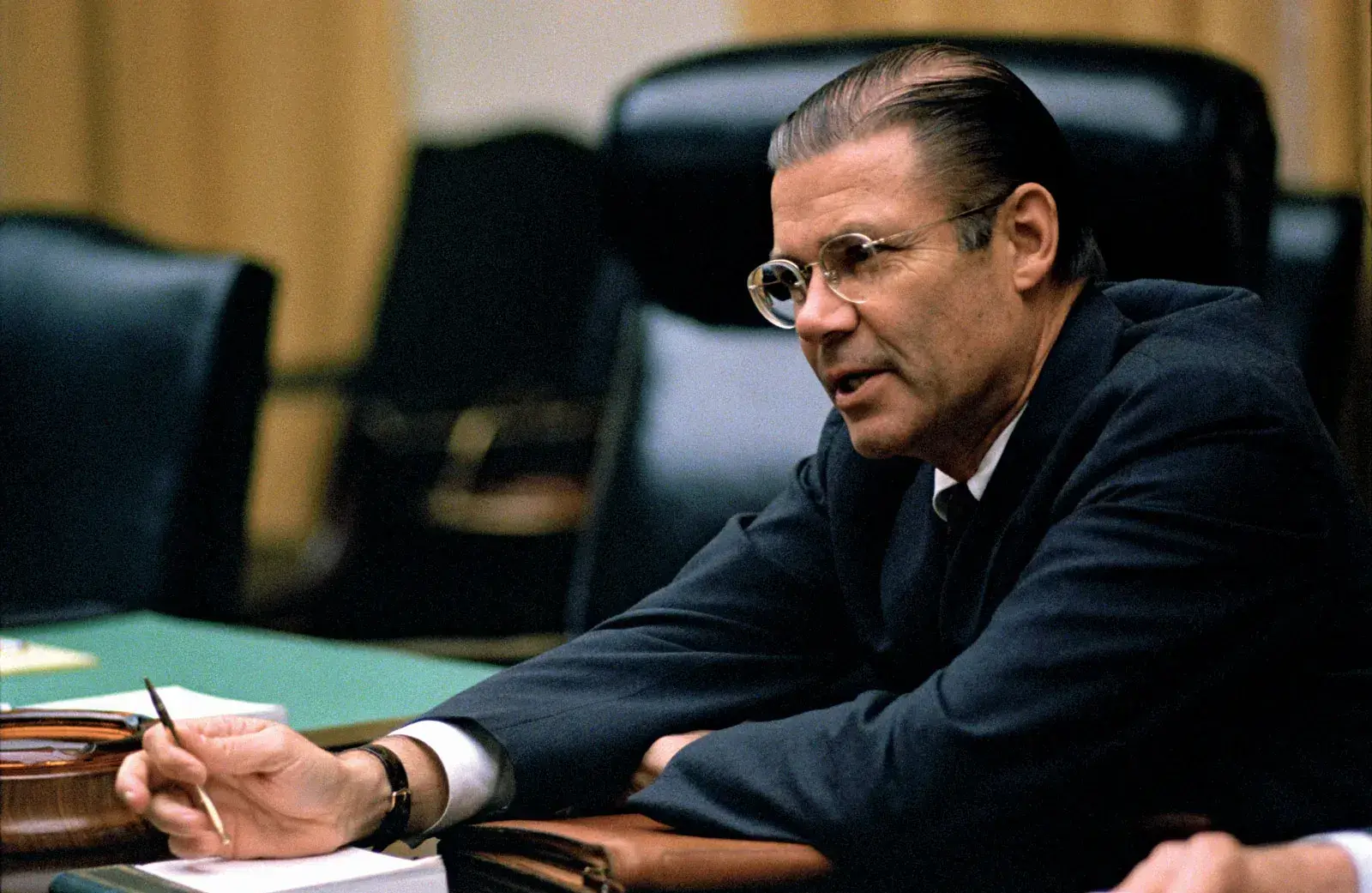
“I know of no one in America better qualified to take over the post of Defense Secretary than Bob McNamara,” wrote Ford chief executive Henry Ford II in late 1960.
It had been only fifty-one days since the former Harvard Business School whiz had become the automaker’s president, but now he was off to Washington to join President-elect John F. Kennedy’s brain trust. At 44, about a year older than JFK, Robert S. McNamara had forged a reputation as a brilliant, if arrogant, manager and problem-solver with a computer-like mastery of facts and statistics. He seemed unstoppable.
Yet, despite sterling qualifications to run the Pentagon, McNamara would encounter a problem his managerial acumen could not solve — at least not in the way the Cold War consensus may have demanded. Under two presidents, he sank the country into an unwinnable war in Vietnam. He misled the American people, drove decisions that brought about the deaths of 58,000 U.S. service members and millions of Vietnamese, and lived out his last decades a tormented man, wracked by guilt and regret but never formally apologizing for the epic disaster he helped create in Southeast Asia, as his personal correspondence and his public memoirs attest.
In all his charts and graphs and body count stats, McNamara failed to measure what mattered most: the unrelenting determination of the Vietnamese people to liberate their country from foreign occupation.
This is, of course, a familiar story told many times before. McNamara’s memoirs were published in 1995, two years after Deborah Shapley’s biography. An anguished McNamara, then in his late eighties, appeared in Errol Morris’ documentary Fog of War in 2003. Library shelves are groaning under the weight of Vietnam studies.
Thus, breaking new ground here may seem rather difficult. Yet the brothers Philip and William Taubman have written “a new history,” to borrow the subtitle of their portrait of the reviled defense secretary, that “benefited from access to materials previously unavailable to McNamara biographers,” including a trove of personal letters exchanged between McNamara and his mother, wife, and Jackie Kennedy.
There is never a bad time to cast a fresh pair of eyes — or, in this case, two pairs of eyes — on such an important story, and the authors succeed in revealing the obscure sides of McNamara’s complicated persona in their humane, yet unsparing, “McNamara at War.” We are in reliable hands: Philip Taubman covered U.S. foreign policy at The New York Times for three decades and authored three books on the Cold War. Older brother William, a career academic, has written biographies of Gorbachev and Khrushchev. The latter earned a Pulitzer Prize.
This book lands as an overdue debate roils Washington concerning the United States’ global role. Questions straight from the Vietnam Era demand our attention. What are the core national interests? Which ones are peripheral? What are the limits of American military power? Thus, the rise and fall of Robert McNamara as told by the Taubmans is as relevant as ever. Their “new” political-psychological portrait poses questions McNamara spent his post-Pentagon years struggling to answer. Namely, why did the government’s sharpest minds around Presidents Kennedy and Johnson screw up so badly?
The Robert McNamara who appears in these pages was no strident ideologue as he prepared to escalate the war in 1964-65, although he neither questioned the validity of the Domino Theory nor doubted the importance of upholding U.S. Cold War credibility.
Perhaps more importantly, McNamara — and he was hardly alone in this — conflated loyalty to the president with loyalty to the Constitution. The authors also compel us to consider the negative influence of his personality, which was not unlike that of the volatile, insecure Lyndon B. Johnson. Driven by ego and fear of failure, McNamara simply could not quit a problem. Yet, as is frustratingly clear in the contemporaneous phone conversations, official memos, and private letters that fill hundreds of the Taubmans’ pages, McNamara from a relatively early stage — autumn 1965 — already harbored serious doubts the war could be won.
Still, he never directly counseled Johnson to withdraw while repeatedly misleading the public about imaginary progress on the battlefield. He chose the path of least resistance, a middle ground between capitulation and an all-out war that might provoke either China or the Soviets to join. The authors’ use of McNamara’s personal highs and lows, related in letters to his tormented family and JFK’s widow, provides a fuller picture of the man, but doesn’t altogether enhance our understanding of what led the Johnson administration to wage war in Vietnam.
McNamara knew almost nothing about Vietnamese culture or history, similar to the ignorance that led the George W. Bush administration to leap headlong into Iraq in 2003. However, he had a chance to at least understand war’s horrors, if at a distance, from his service under General Curtis LeMay during the strategic bombing campaign against Japan in 1945. “His time at Guam deserves greater attention,” the Taubmans contend, referring to McNamara's statistical analysis of aerial bombardment of Japanese cities, “brutal tactics that McNamara favored at the time.”
The March 1945 firebombing of Tokyo killed approximately 100,000 people and left a million homeless. “At least one historian, having noted that McNamara helped ‘kill hundreds of thousands of civilians,’ described him as seemingly ‘impervious to the human cost of his work,’” the authors say. This mechanical, data-driven approach informed McNamara’s war planning 20 years later. It remains astonishing, even after the passage of 60 years, that President Johnson and his chief advisers convinced themselves they were undertaking a “limited” bombing campaign as the Vietnamese shook under the force of B-52 raids. Our leaders lied to the public and themselves.
Even now, the unlearned lessons here are many, which may be why the Taubman’s dedicate their last 100 pages to Robert McNamara’s strained efforts to publicly atone for his crimes after exiting the Pentagon in 1968. It took him decades to do so, a lapse for which his critics never forgave him. Still, the managerial genius brought low by Vietnam hoped his 1995 memoirs would be read widely by policymakers to avoid past mistakes. If read, the lessons weren’t heeded. Vietnam, Afghanistan, Iraq – shall we count the repetitions?
No one should pity the life of Robert McNamara, but his story reinforces the notion that powerful structural forces, such as Cold War ideology or Vietnamese nationalism, can overwhelm or tame an individual’s will to reverse course. Still, McNamara eventually attempted to make amends by admitting what were avoidable mistakes and advocating for the abolition of nuclear weapons.
Readers of “McNamara at War” may compare his self-flagellation with the utter lack of remorse exhibited by two other major figures who recently died. Despite living very long lives, neither Henry Kissinger nor Dick Cheney ever atoned for their crimes. Philip and William Taubman aptly conclude, “More than any other political leader we can think of, Robert McNamara admitted his grave mistakes in the hope of helping others to do better than he did. But the final ironies of his life are that many who continued to pursue peace among peoples and nations… have been no more successful than he was.”