Last month, the Israeli military declared that it had taken “tactical control” of the Philadelphi corridor, the strategically important nine-mile-long and 300-foot-wide buffer zone between Gaza and Egypt.
Israeli officials say that they took this action as part of an effort to decapitate Hamas roughly eight months into this war, claiming that the Palestinians have used this corridor to set up tunnels for funneling arms.
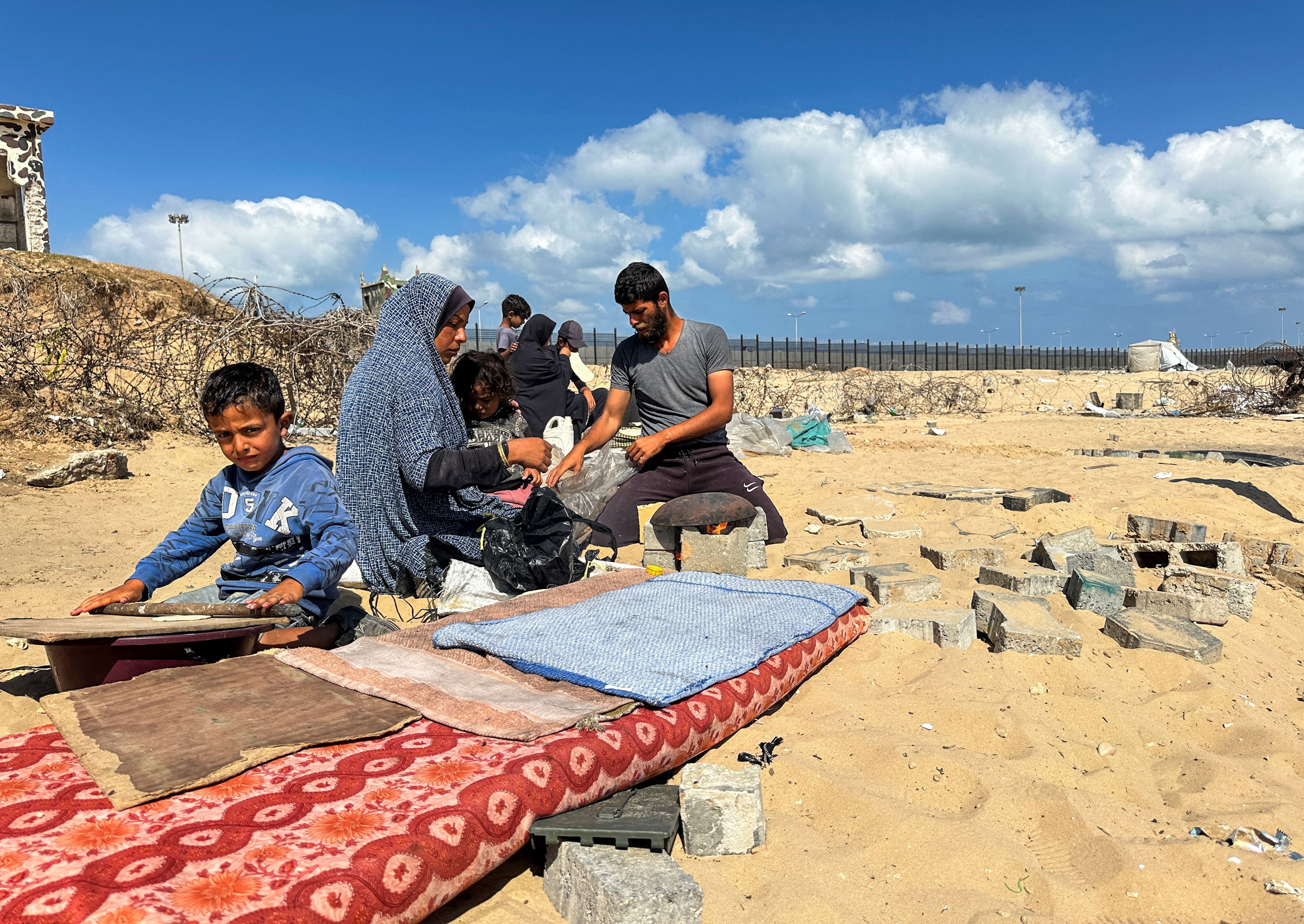
But these tunnels have been used to bring all types of goods and services, not just weapons, into Gaza — even if authorities in Egypt, which has officially been imposing its own blockade on Gaza since 2007, have not been openly admitting so. These tunnels connecting Egypt and Gaza have given the Palestinians in the besieged enclave some sort of a lifeline. Now the blockade will be even tighter and Gaza’s humanitarian disasters are only set to worsen.
“The direct control of the [Philadelphi corridor] by Israel means the complete encirclement of Gaza, which in prior years [the Israelis] left that one part of the borders to a joint Egyptian-Palestinian control. For Palestinians it denies them all hope of an Israel-free part of their borders,” Nabeel Khoury, former deputy chief of mission at the U.S. Embassy in Yemen, told RS.
“Israel’s takeover will make it that much harder for humanitarian aid to get through. Israel’s right wing is getting its desired goal here: Full encirclement of Palestinians and denial of all means of livelihood — in other words a step closer to driving out whoever is still alive once this war ends, if it ever does,” added the former US diplomat.
The situation in the Philadelphi corridor has potentially huge implications for the future Israel’s cold peace with Egypt. Overall, the past eight months of warfare in Gaza have created difficult dilemmas for Egypt’s government.
Officials in Cairo have spent months sounding the alarm about the Israeli military’s advance toward the Egypt-Gaza border, fearing that this war will drive Palestinians into Egyptian territory. At the same time, President Abdel Fatah el-Sisi’s government has been seeking to avoid an escalation of tensions with Israel’s government while simultaneously trying to keep a lid on growing anger among Egyptian citizens who are staunchly pro-Palestinian.
In taking control of the Philadelphi corridor, Israel is violating the 1979 peace accord with Egypt, further complicating its already frosty relationship with Cairo. Egypt and Israel’s peace accord permits each side to deploy a small military or border security presence in this demilitarized zone, yet only through a mutual agreement can the number of troops in the Philadelphi corridor to be adjusted. At the time of the peace accord’s implementation in 1979, Israel had been occupying Gaza with troops on the ground since 1967. Those Israeli military forces as well as Israeli settlers didn’t withdraw from the coastal enclave until 2005.
“An already icy relationship is heading for deep freeze,” is how Patrick Theros, the former U.S. Ambassador to Qatar, described the state of Egyptian-Israeli affairs in an interview with RS. “Neither government has an interest in breaking the formal ties between the two countries. Internal pressures have mounted in Egypt and will only get worse. The current regime in Cairo has shown it can suppress demonstrations effectively, but there has to be a point where Sisi must do something to placate public opinion. I don't know when, where, or what. But it must come,” added Theros.
On May 24, two Egyptian soldiers died amid a clash between the Egyptian and Israeli militaries near the Egypt-Gaza border. Although both Cairo and Tel Aviv took quick steps to contain potential fallout from the deadly episode, the clash illustrated the fragility of Egyptian-Israeli relations amid this volatile period. As demonstrated by the reactions on social media, the Egyptian soldiers’ deaths also led to increased rage among the Egyptian public.
Egypt’s weaknesses
Israel’s control of the Philadelphi Corridor and, more broadly, the war in Gaza have put Egypt’s government under much pressure from various sides. The overall situation has seemingly left the Sisi government feeling humiliated with its vulnerabilities increasingly exposed. Ultimately, with the Egyptian army heavily dependent on the U.S. for financial and military assistance and unable to credibly challenge the Israeli Defense Forces (IDF), there is not much Egypt can do to counter Tel Aviv.
Yet, with its own population increasingly angry, Sisi can’t ignore domestic pressure at a time when other factors such as Egypt’s deteriorated economy challenge his regime’s stability and legitimacy.
“[The Gaza] crisis has highlighted Egypt’s weak hand. It cannot threaten Israel with anything Israelis will take seriously without threatening U.S. ties and assistance. It cannot do the only thing the Israelis have demanded of Egypt: accepting the millions of Gazans Israel wants to expel from the Gaza Strip. Other than maintaining the status quo, Egypt has nothing to offer. It has connectivity with Hamas in Gaza, but the Israelis do not value that,” Theros told RS.
Israel’s Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu vows to continue this war until Hamas is defeated, which could extend the fighting into 2025. Yet prolonged warfare in Gaza and more Palestinian suffering in the enclave means that Egypt’s leadership will face intensified pressure from its own population, especially if Palestinians in large number flee Gaza for the Sinai or if trigger-happy IDF troops kill more Egyptian soldiers. How these scenarios would impact the Camp David Accord remains an open question.
What is clear, however, is that the government in Cairo wants this war in Gaza to end as soon as possible to relieve the Sisi regime of these pressures. This is why Egypt is working hard with Qatar to broker a lasting ceasefire. Unfortunately, Cairo and Doha’s diplomatic efforts to bring this horrific war to an end have yet to prove successful. Until that outcome is achieved, Egypt’s government will continue to remain extremely vulnerable and appear weak.
- Why Arab leaders aren't helping the Palestinians in Gaza ›
- Will Egypt suspend the Camp David Accords? ›
- Why Egypt can't and won't open the floodgates from Gaza ›
- Why does Egypt fear evacuating Gaza? ›
- Gantz Quits the War Cabinet: Sizzle or Fizzle? | Responsible Statecraft ›
- Egypt's energy gamble has left it beholden to Israel | Responsible Statecraft ›