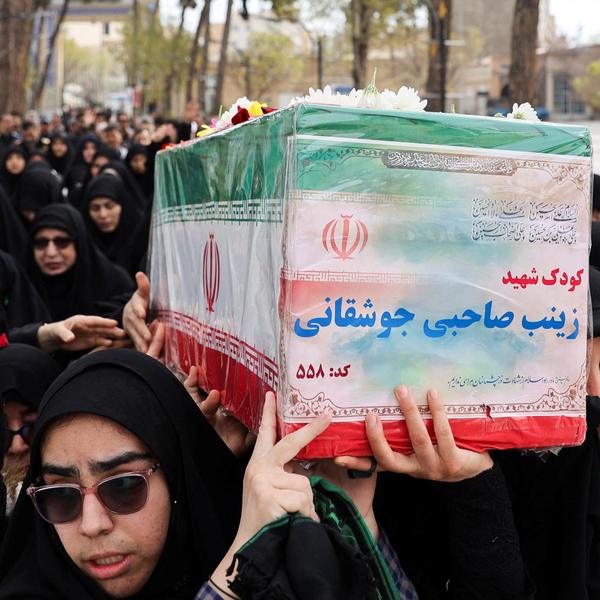
In late spring of this year, American diplomats in Jerusalem drafted an urgent cable. The war in Gaza, coupled with Israel’s decision in March to block all forms of aid from entering the strip, had left the region on the brink of disaster. A famine was looming, and the U.S. wasn’t doing anything about it.
But that cable never got back to Washington. In fact, it’s not clear whether it even reached the desk of Mike Huckabee, the U.S. ambassador to Israel. In its place, David Milstein — a senior adviser to Huckabee — sent a cable that sounded like “an advertisement for the Gaza Humanitarian Foundation,” according to two State Department officials with knowledge of the incident.
“It sounded like a propaganda statement,” one official told Responsible Statecraft. As mainstream aid groups condemned GHF for endangering Palestinian aid seekers, Milstein’s report praised the organization for meeting a “humanitarian need.” Roughly two months after Milstein sent his cable, the world’s leading hunger monitor declared a famine in Gaza for the first time.
The previously unreported incident highlights the extent to which Milstein has exerted influence over U.S. policy despite his seemingly modest position as an ambassador’s adviser. In the first eight months of the Trump administration, Milstein has become something of a pro-Israel enforcer, reaching across the State Department to steer U.S. policy and contest any information that casts Israel in a negative light, according to current and former State Department officials who spoke with Responsible Statecraft.
In an effort to strengthen U.S. support for Israel, Milstein has confronted colleagues he viewed as insufficiently pro-Israel, removed content critical of Israel from press statements as well as a major annual human rights report, and tried to get the U.S. government to refer to the West Bank as “Judea and Samaria,” a controversial term often used by supporters of Israeli annexation of the region. Prior to his current role, Milstein worked in various capacities with pro-Israel Republican politicians like Sen. Ted Cruz (R-Texas) and GOP Florida Gov. Ron DeSantis.
Milstein’s efforts first broke into public view in July, when the State Department fired Shahed Ghoreishi, who was serving as the department’s lead press officer for Israeli-Palestinian affairs.
Milstein, who is the stepson of conservative radio host Mark Levin, had on several occasions butted heads with Ghoreishi over press statements relating to Israel. Following a disagreement over whether to say the U.S. opposed forced displacement of Gazans — a point on which neither President Trump nor his peace envoy Steve Witkoff have expressed a consistent view — Ghoreishi was fired without explanation.
In an interview with Responsible Statecraft, Ghoreishi claimed that Milstein had “reached out to Secretary [of State Marco] Rubio’s office and used his influence” to get Ghoreishi fired. Milstein did not respond to a request for comment.
In a statement, State Department Principal Deputy Spokesperson Tommy Pigott said the department "has zero tolerance for employees who commit misconduct by leaking or otherwise disclosing confidential deliberative emails or information," adding that the comments contained in this article are "outrageous and dishonest."
"David Milstein is a strong and valued advocate for the policies of the Trump Administration and for the American people," Pigott said.
The Ghoreishi dispute left many in the State Department on edge. Milstein “actually did get someone fired,” a State Department official said. “Is he gonna find some way to throw me under the bus?”
How to blind an embassy
The roots of Milstein’s influence date back to the first Trump administration. When the U.S. decided to move its embassy from Tel Aviv to Jerusalem, the new facility swallowed up the American consulate in Jerusalem, which had previously acted as a de facto embassy to the Palestinians, with separate channels back to Washington.
This policy increased the importance of the U.S. ambassador to Israel, who now had direct control over the Palestinian section, meaning that they could block unwanted information from reaching Foggy Bottom. During the first Trump administration, “anything they didn’t like just didn’t go out,” recalled Mike Casey, a former foreign service officer who worked in the embassy from 2020 to 2024. “It never even gets to the ambassador for him to look at it and say ‘no.’” At the time, this largely meant blocking any cables noting concerns about Israeli settlements in the West Bank.
Before Milstein there was Aryeh Lightstone, the chief of staff to Trump’s first term ambassador to Israel, David Friedman. (Milstein also served as an assistant to Friedman, though his influence remained limited.) Lightstone acted as a gatekeeper for Friedman, blocking any reporting on issues like alleged settler violence before it even reached the ambassador’s desk, according to Casey, who described Lightstone’s role as “unusual.”
“[Chiefs of staff] move paperwork and they do help with priorities and that sort of thing, but they're not there to suppress reporting that they don't agree with,” Casey told Responsible Statecraft. “For the ambassador to get involved [in policy debates] is normal. For the chief of staff to be doing it is unusual.”
When the Biden administration took over, the Palestinian Affairs section of the embassy regained its autonomy, allowing it to communicate with Washington without having to go through the ambassador to Israel. During the Gaza war, Amb. Jack Lew blocked his own staff from reporting “anything critical of the Israelis,” but the Palestinian office maintained a certain degree of independence, according to Casey.
When Trump returned to office this year, that independence disappeared once more, and Milstein stepped into Lightstone’s old role as the ambassador’s right-hand man. Lightstone, for his part, found his way back into government as an adviser to Witkoff. In that position, Lightstone has acted as a mediator between the U.N. and the GHF, drawing controversy earlier this year for “his refusal to hear criticism of GHF” from Western officials, according to Haaretz.
‘Raising concerns is considered insubordination’
When it comes to dissent, the Trump administration set the tone early. Before Trump’s inauguration, a low-level transition official met with State Department staffers and “asked who the PLO supporters were” in the department, a State official said, using the acronym for the Palestine Liberation Organization, which currently dominates the Palestinian Authority.
The incident, coupled with promises from political appointees to ferret out the “deep state,” raised concerns within the department. Particularly worried were officials who had signed onto “dissent cables” — a protected mechanism for contesting official policy internally — related to Gaza. (No officials are known to have been fired for signing onto a dissent cable.)
Staffers with relatively even-handed views of the Israel-Palestine conflict now find themselves afraid to speak up internally, leaving a great deal of latitude to some of Trump’s more emphatically pro-Israel appointees. Milstein has relished the opportunity to make his influence felt across the department.
In July, when Ireland was weighing whether to ban trade with Israeli settlements in the West Bank, Milstein drafted a statement condemning Ireland for even considering the move, according to sources who spoke with the Washington Post. The effort “alarmed U.S. diplomats in Europe,” the Post reported, noting that the envoys wanted to discuss the issue privately with Irish officials rather than creating a public row with a close European partner. The diplomats won out in the end, according to the Post.
But career officials haven’t always been so lucky. When Milstein began his current job, he immediately launched his own review of the State Department’s human rights report about Israel and the Palestinian Territories. The original version, which had been developed by career officials and approved during the Biden administration, contained significant criticisms of both Israel and Hamas’s records on human rights. But when Milstein returned his own edits, “a lot of the information critical of Israel was removed,” a State Department official said. The final version focused mainly on criticizing Palestinian groups and was only nine pages long — nearly 100 pages shorter than the one issued by the Biden administration the previous year.
In his efforts to advance pro-Israel views within the State Department, Milstein often relies on questionable sources for news and information, an official said. One such source is Palestinian Media Watch, which has drawn criticism for its emphatically pro-Israel stances and its alleged tendency to cherry pick controversial quotes from Palestinian Authority officials. “He’s talking about it like it’s a credible news source” without indicating “how biased it is,” the official added.
A senior State Department official described Milstein’s approach as emblematic of a broader culture of fear within the second Trump administration. “I worked for Trump appointees in the first administration, and it is fundamentally different this time around,” the official said. “Raising concerns is considered insubordination. That language is clear from the top down.”