Positive perceptions of the United States by the citizens of Washington’s most important Western allies across the globe have fallen to record lows, in some cases even lower than during the nadir of the George W. Bush administration after its invasion of Iraq. The findings, published this week by the Pew Research Center’s Global Attitudes project, reveal consistently unfavorable opinions of both the United States and President Donald Trump’s leadership.
A majority of respondents in 12 of the 13 nations covered by the survey — South Korea being the sole exception — said they held a negative opinion of the United States. A median of only 34 percent of all respondents expressed favorable views of the U.S.
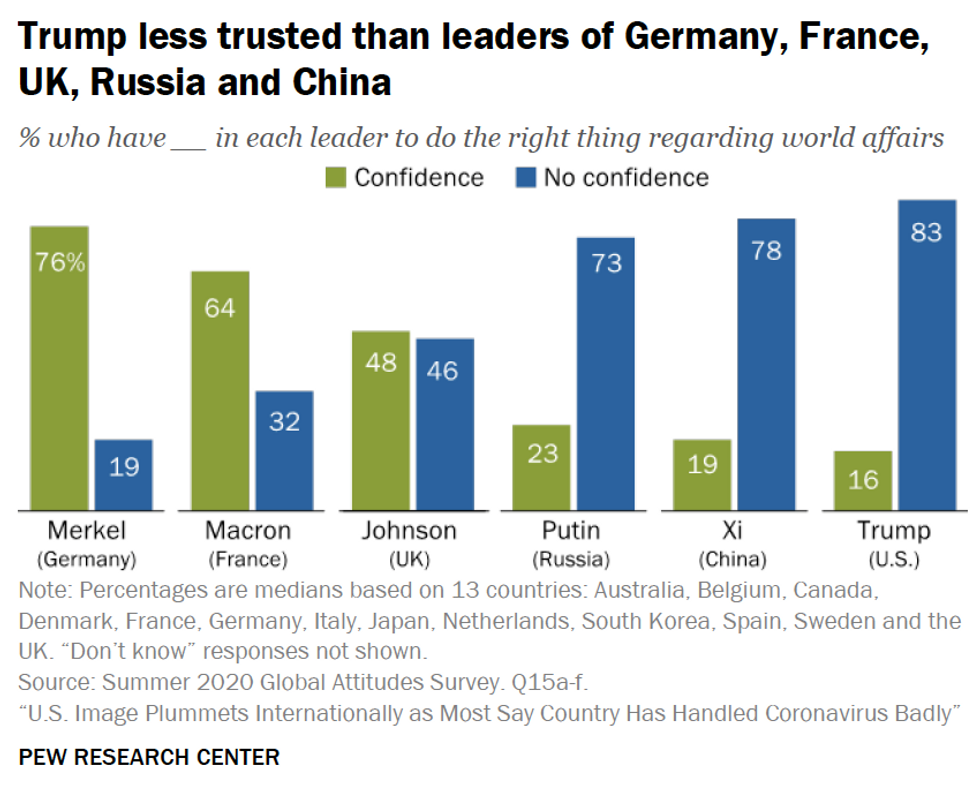
The leadership of President Trump was viewed even more negatively, particularly in western Europe, with a median of a mere 16 percent of respondents saying they had “some” or “a lot of” confidence in the U.S. president “to do the right thing in world affairs.”
In comparison to other world leaders — Germany’s Angela Merkel, France’s Emmanuel Macron, the United Kingdom’s Boris Johnson, Russia’s Vladimir Putin, and China’s Xi Jinping — Trump was found to inspire the least confidence — although Putin and Xi also fared relatively poorly — among European respondents.
“These numbers are predominantly a response to Trump’s foreign policy,” Steve Kull, Director of the Program for Public Consultation at the University of Maryland told Responsible Statecraft. “Withdrawing from the World Health Organization, aspects of Trump’s own personality, and the coronavirus pandemic are all likely contributors” to these results, according to Kull.
The Global Attitudes project, which has been regularly polling international perceptions of the U.S. and other major foreign policy issues since the early 2000s, was released Wednesday but has received little media coverage.
The survey covered several regions. European countries surveyed included the United Kingdom, France, Germany, Spain, Italy, the Netherlands, Belgium, Sweden, and Denmark. The poll also included Japan, South Korea, Australia, and Canada. Altogether, over 13,000 respondents in the 13 countries were surveyed between June 10 and August 3.
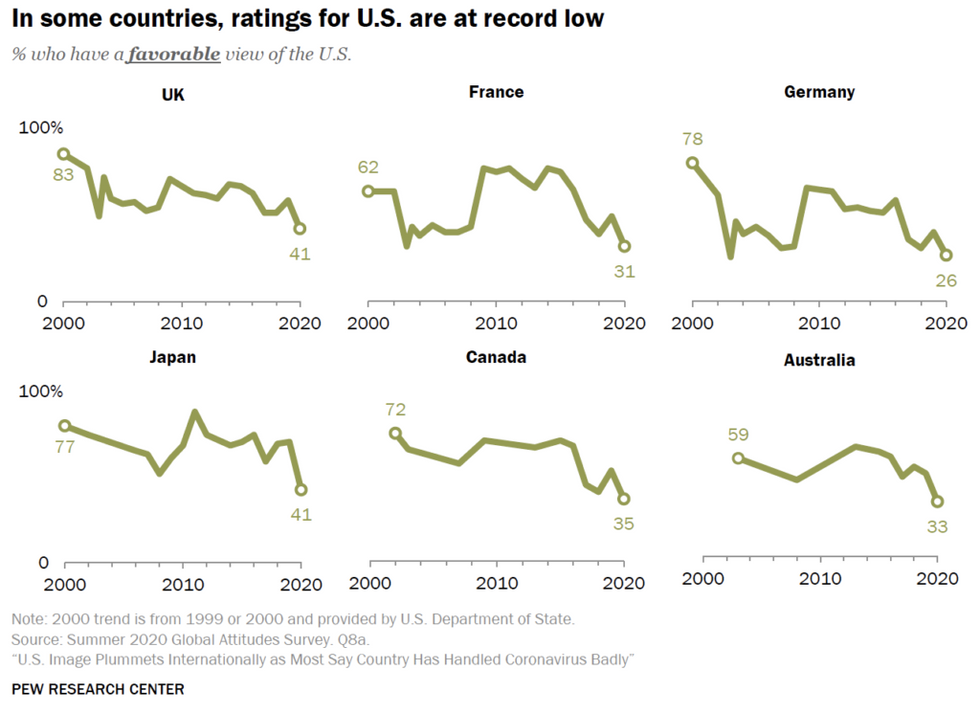
With the exception of Sweden, Washington has collective-defense agreements with all of the countries covered by the poll, which requires them to consider an attack on the United States as an attack on them and vice versa. Record low public approval for the United States in those countries, if it persists, could have important implications for Washington’s defense posture overseas.
In six of the 13 countries — the United Kingdom, France, Germany, Japan, Canada, and Australia — Washington’s image fell to its lowest point since Pew began conducting these surveys, substantially lower in Japan, Canada and Australia than even after the 2003 U.S. invasion of Iraq.
As noted by Kull, this year’s record declines could be attributed in part to perceptions of the country’s — and Trump’s — handling of the coronavirus pandemic. The United States is fast approaching 200,000 deaths attributed to the virus, the world’s highest total death toll.
Respondents in all 13 countries surveyed rated Washington’s response to the pandemic as the worst. They said their own countries, as well as the WHO, had performed more effectively.
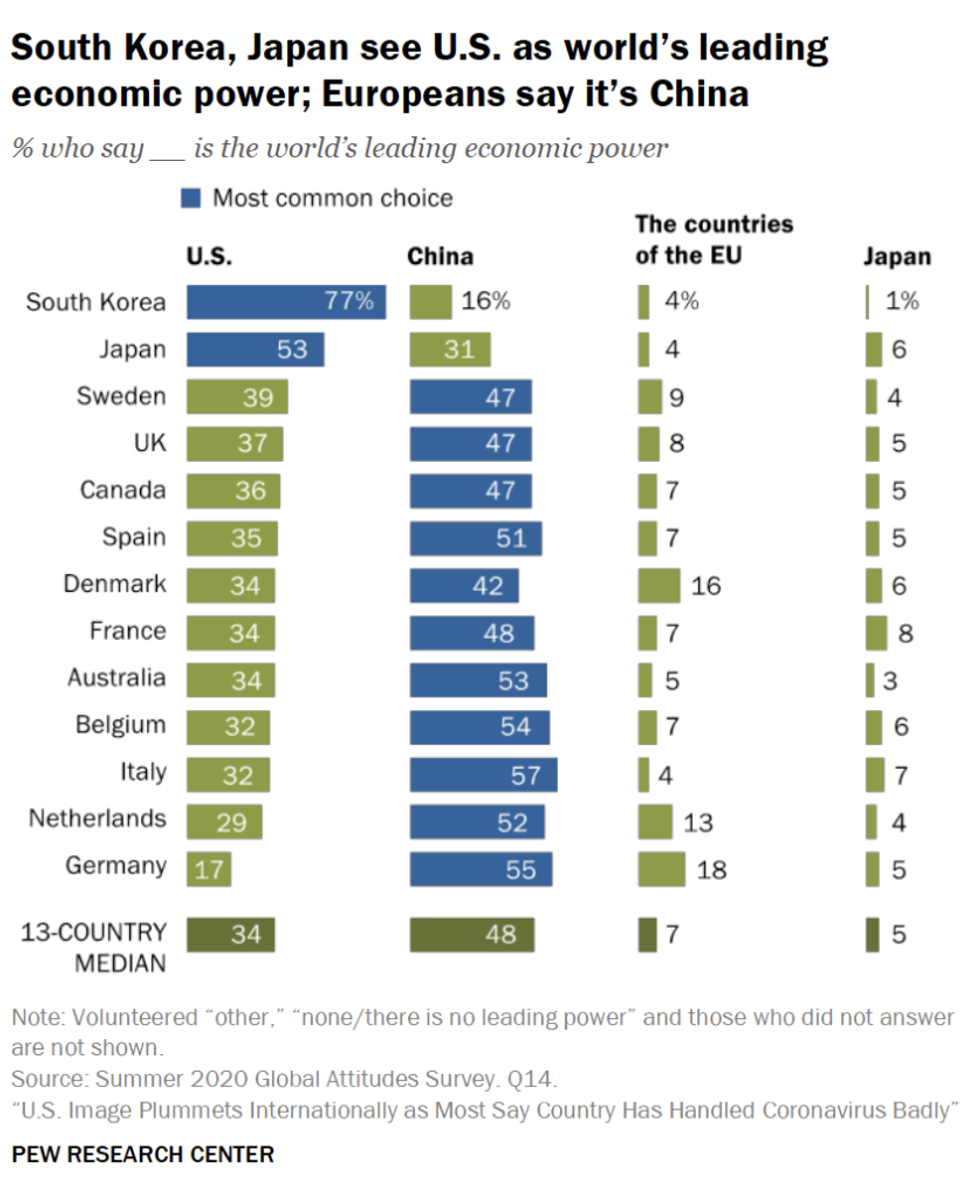
The perception of U.S. economic strength also appears to have suffered, according to the survey results. Of the 13 countries, majorities in only South Korea and Japan said they considered the United States to be the world’s leading economic power. Pluralities or majorities in the other 11 nations rated China as the world’s leading economic power.
Writing in the Washington Post, Daniel Drezner, who teaches international relations at Tufts University, found this result particularly concerning. “Despite Trump’s claims about building the greatest economy in history, and despite a two-year trade war,” he wrote, “a plurality of respondents believe that China is now the world’s most powerful economy.”
Kull stressed that the plunge in the U.S. image documented by the latest poll is not necessarily irreversible. Despite the low ratings of the country that followed the Iraq invasion, which in some countries dipped to levels not far from where they currently stand, positive views of the United States rebounded in most countries with Obama’s election.
Similarly, trust in the U.S. president “to do the right thing regarding world affairs” rose sharply, at least initially, when Obama succeeded Bush in 2009. Kull expressed confidence that a similar recovery in global favorability towards the U.S. will occur if Joe Biden defeats Trump in the presidential election this November.
To see the remainder of the survey’s findings, read it here.