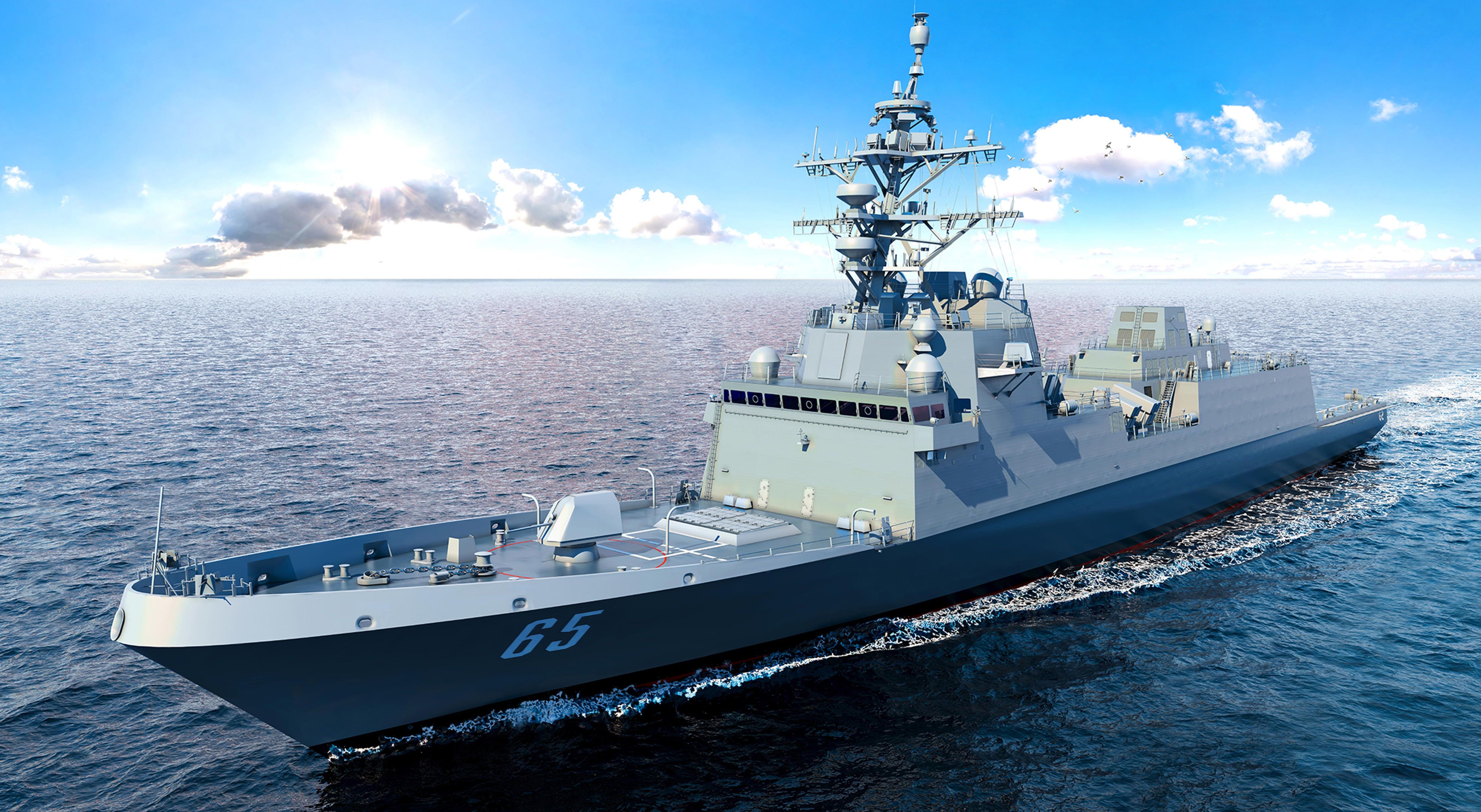
The United States Navy has a storied combat record at sea, but the service hasn’t had a successful shipbuilding program in decades. John Phelan, the secretary of the Navy, announced the latest shipbuilding failure by canceling the Constellation-class program on a November 25.
The Constellation program was supposed to produce 20 frigates to serve as small surface combatant ships to support the rest of the fleet and be able to conduct independent patrols. In an effort to reduce development risks and avoid fielding delays that often accompany entirely new designs, Navy officials decided to use an already proven parent design they could modify to meet the Navy’s needs. They selected the European multi-purpose frigate design employed by the French and Italian navies.
Navy leaders made the decision to speed up the process with the Constellation program because it was supposed to fill the capability gap created by the failure of the Littoral Combat Ship program. The LCS was intended to be the Navy’s affordable small surface combatant ship of the future, but it ended up failing spectacularly. Engineers were never able to get the ship’s mission hardware to work properly. The ships also suffered a string of embarrassing mechanical breakdowns.
The decision to use a proven design for the new program was sound. Defense policymakers typically pursue clean-sheet designs because the contractors can maximize their financial gain through the research and development process. But the Constellation-class program now clearly demonstrates how the national security establishment’s natural proclivity to make simple things complicated remains firmly in place.
The Constellation-class program failed because rather than simply building the ships as designed in Europe, American naval engineers effectively tore up the blueprints and designed a new ship. The U.S. Navy has different mission requirements than its European counterparts, so the ship’s design did need some modifications. Officials sold the idea of the Constellation-class program in part by saying the American version would have 85% commonality with the European version. They then lengthened the hull by nearly 24 feet, redesigned the bow, completely redesigned the ship’s superstructure, and added approximately 500 tons of displacement. The American design today has only 15% commonality with the original.
Navy officials compounded all those problems by committing one of the major deadly acquisition sins: starting production before completing the design. The practice of concurrency, the official term for the overlap of development and production, has been described by one former Pentagon acquisition chief as “malpractice.” Building a ship, tank, or aircraft before the constituent technology has been proven through testing all but guarantees the program will go over budget and fall behind schedule, yet it happens all the time.
Cost growth in shipbuilding so far this century paints a stark picture. Each Littoral Combat Ship was expected to cost $220 million when the program began in 2002. By the time Navy officials gave up on the program, the cost of each hull had grown to over $600 million.
Even worse was the Zumwalt-class destroyer. Officials planned to build a fleet of 32 ships with an anticipated cost of $1.5 to $1.8 billion per ship. The program was cancelled after only three ships were built because the intended main weapon system proved to be cost prohibitive. The remaining ships currently lack a clear mission despite their nearly $8 billion price tag.
The Navy sunk nearly $9 billion into Constellation-class program before its cancellation.
The financial cost of failed programs is obviously significant, but so is the opportunity cost. The Navy doesn’t just invest taxpayer money into these programs, it also invests time. The Littoral Combat Ship program used up approximately 15 years of shipbuilding time. The Constellation-class program has used an additional decade. Both add up to a quarter century of now wasted shipbuilding time during which the existing ships need to have their service lives extended. It’s obviously too early to tell how long it will take officials to get yet another new ship into service. Using history as a guide, a new ship shouldn’t be expected to be in service until the middle of the 2030s at the earliest.
The on-going Littoral Combat Ship and Constellation-class saga should serve as a case study for all defense policymakers. These shipbuilding failures demonstrate the importance of getting things right from the beginning in acquisition programs. Absorbing a single failure is difficult in both time and money. Sailors will have to work harder to keep the Navy’s aging and shrinking fleet afloat to meet the nation’s security needs. Recent history has shown how overworking sailors creates dangerous situations like deadly collisions at sea.
- Why would the Navy buy more ships when it is incapable of competently managing what it has? ›
- Facing the hard facts about the 'world class' US Navy ›
- In Red Sea, US Navy paying the price of shipbuilding failures ›
- Trump's big, bad battleship will fail | Responsible Statecraft ›