Back in 2009, I was in Strasbourg for a “No to NATO” protest. Running from tear gas and being escorted out of a French military base by German soldiers, I spent some time with Malalai Joya—then the youngest member, and one of the few women, in the Afghan parliament.
It was eight years into the U.S. occupation of Afghanistan, and President Obama, after sending 17,000 additional troops, was publicly debating whether to launch another new troop surge there.
As a woman in parliament, Malalai faced death threats and attacks. She’d been forced into hiding and could not appear in public in her own country. If the United States pulled out, I asked, what would happen to people like her?
She told me then, and the words stuck.
“We in civil society,” she said, “face three enemies in my country: the Taliban, the warlords disguised as a government, and the U.S. occupation. If you in the U.S. can mobilize to get the U.S. and NATO troops out of my country, we’d only have two.” (Four years later, she repeated that view in The Nation.)
A weak, unclear agreement
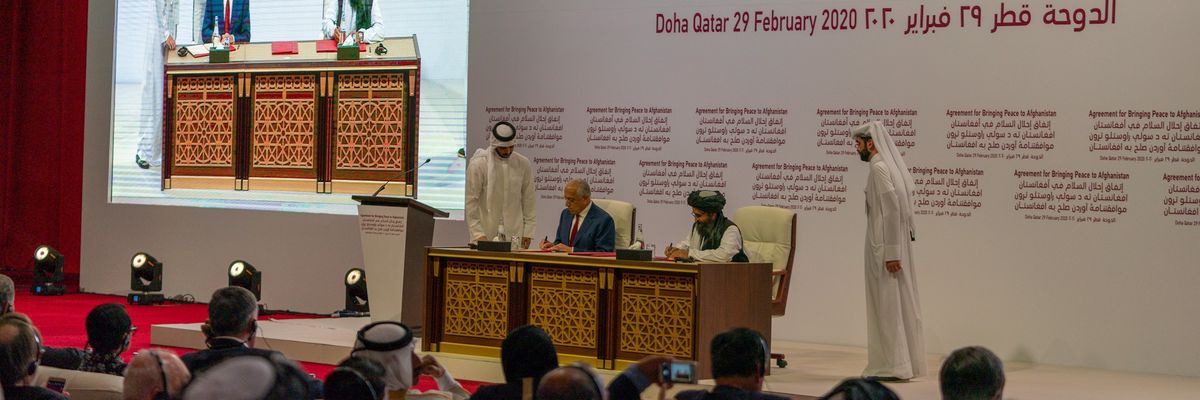
And now, Washington has signed a deal with the Taliban that may at least begin the process of pulling U.S. troops out of Afghanistan.
In return for Taliban promises to break ties with al Qaeda and ISIS, and to begin negotiations with the U.S.-backed Afghan government, the United States agreed to withdraw all troops within 14 months—4,000 or so in the next four and a half months, and the rest, “with the commitment and action” by the Taliban, within another nine months.
Little is clear about the agreement. What we do know is that this is not a peace deal. It does not promise even a long-term ceasefire or an end to war in Afghanistan, let alone guarantee peace, security, and human rights for the people of that war-devastated country. Already, U.S. airstrikes and numerous Taliban attacks have occurred in the wake of the deal’s announcement.
Rep. Barbara Lee (D-Calif.), who cast the only dissenting vote against the war when Congress authorized it immediately after the 9/11 attacks, recognized the insufficiency of the agreement, signed in Doha on February 29. It “leaves thousands of [U.S.] troops in Afghanistan and lacks the critical investments in peacebuilding, human-centered development, or governance reform needed to rebuild Afghan society,” she said.
She’s right. Washington owes the people of Afghanistan an enormous debt to help rebuild their country—though there’s little political will in Washington for it, and there are serious doubts about whether the corrupt Afghan government could handle it. This deal appears to address only troop levels, leaving those thornier but crucial issues untouched.
And yet it’s also true that this agreement, if implemented, would represent a critical first step—a profoundly insufficient but necessary step—towards security in the country. As Malalai Joya recognized, withdrawing foreign troops would eliminate one of the three enemies of the Afghans struggling to survive these decades of war. Even if the withdrawal is only partial, it would still reduce the attacks, bombings and drone strikes of at least one of those armed forces.
Nonetheless, the agreement is filled with weaknesses.
The U.S.-backed Afghan government, long known for unceasing corruption, as well as for harboring warlords responsible for the same kind of attacks on civilians as the Taliban, was not included in the negotiations. Complicating matters, two rival candidates—incumbent president Ashraf Ghani and challenger Abdullah Abdullah—have now both claimed victory in Afghanistan’s recent presidential election, so choosing a negotiating team is delayed. Nothing is certain.
Longer term, the lack of representation of Afghan society in the process—including women, youth, unions and other civil society organizations—also undermines the deal’s credibility. That denial of a place at the table for women, non-military actors and others, however, is all too standard in negotiations to end wars. It’s one of the factors that makes transitions from short-term ceasefire to long-term peace so difficult.
Rights never realized
Whatever else happens, a U.S. pullout will not leave Afghanistan at peace. Fighting on some level will almost certainly continue. The Taliban, which now controls or contests more than half the country but has less influence in cities, will probably become more influential.
What would this mean for Afghan women?
First, it’s important to remember that the writ of the post-2001 Afghan government, installed and kept in power by the United States and a NATO-led alliance, barely reaches beyond the city limits of Kabul, Kandahar and a few other cities. And only about 25% of Afghans live in cities—the vast majority are in small towns and tiny villages.
For some city residents, certainly, the formal gains for women’s rights in the Afghan constitution—the right to work, to vote, a place in the parliament—were life-changing. But those rights have remained out of reach for many even in the cities, with a government largely opposed to or reluctant to enforce women’s rights. And most Afghan women live in the countryside, where the new constitution, with its official guarantees of rights for women, never had much impact.
Make no mistake: Life under Taliban rule was terrible, especially for women and children. The problem is that years of U.S. occupation changed far too little. Today, according to the CIA, Afghanistan still ranks first in the world in infant mortality.
There is no guarantee that the withdrawal of U.S. troops will create conditions for new cultural, social and political struggles inside Afghanistan. But we do know that perpetuating the current levels of fighting, in which civilians continue to suffer the highest levels of death and injury, pretty much guarantees that those struggles, which could result in real change in the lives of far more Afghan women and indeed all Afghans, will never take hold.
Trump’s motives
Another thing is certain: Donald Trump deserves no kudos for agreeing to the deal.
There is no question his motives are self-serving and political, not humanitarian or even strategic. After high-profile foreign policy failures regarding Iran, North Korea, and Israel-Palestine, and with the stock market still reeling from the coronavirus catastrophe, Trump’s election slogans of prosperity and peace don’t look so good. So redirecting away from prosperity, to the false claim that he is ending our endless wars, may be his newest ploy.
For all his talk about “ending” the Middle East wars, Trump has actually sent thousands more troops to that region in the three years he has been in office. He is escalating, not ending the global war on terror, and that remains true even if he withdraws troops from Afghanistan. Trump has made clear his inclination to keep Special Forces operators in Afghanistan, regardless of what the agreement says.
As Barbara Lee reminds us, “there is no military solution to the conflict in Afghanistan.”
So while the U.S.-Taliban deal will not itself bring peace—and while there is no reason to trust Trump’s motives or commitment to the deal—the fact remains that withdrawing even some of the U.S. troops, planes, drones and bombers from Afghanistan will reduce the killing of Afghans by U.S. forces.
After 18 years of killing, there’s a lot more work ahead. But this move, which could reduce the number of victims, is worth supporting as a first step.
This article has been republished with permission from Foreign Policy in Focus.