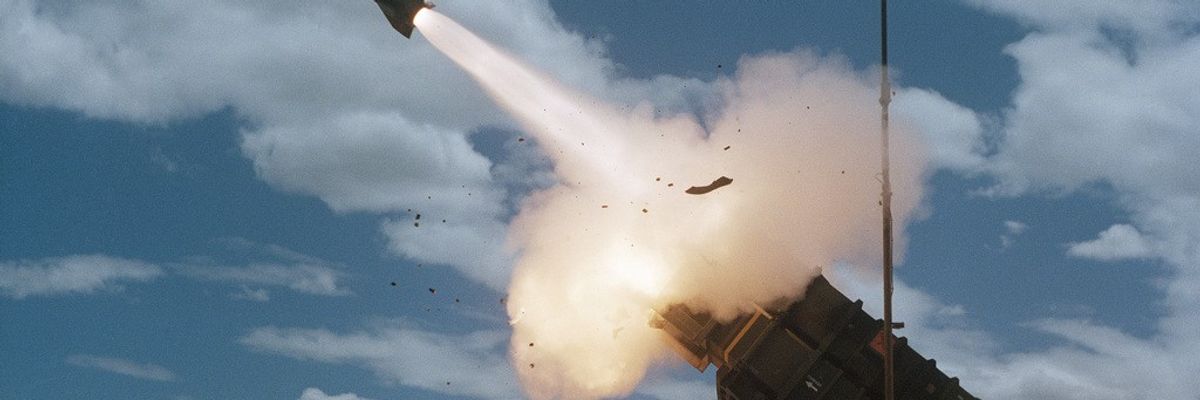
Reports are circulating that the Biden administration is poised to send Patriot missile systems to Ukraine. The Patriot is a sophisticated U.S. designed and manufactured (Raytheon) system whose primary function for the U.S. military is for tactical surface-to-air anti-ballistic missile (ABM) capability.
According to Raytheon:
Global Patriot™ Solutions is a missile defense system consisting of radars, command-and-control technology and multiple types of interceptors, all working together to detect, identify and defeat tactical ballistic missiles, cruise missiles, drones, advanced aircraft and other threats. Patriot is the foundation of integrated air and missile defense for 17 nations.
Since its use in the first Persian Gulf War, the United States has sold/shared Patriot systems to the armed forces of the Netherlands, Poland, Germany, Japan, Israel, Saudi Arabia, Kuwait, Taiwan, Greece, Spain, the United Arab Emirates, Qatar, Romania and Sweden. President Trump took two Patriot missile batteries out of Saudi Arabia during his term reportedly over an oil production dispute, but the move came as the U.S. military was shifting other assets to Iraq and Syria as our troops were coming under fire there.
The plans to send the Patriot to Ukraine is a big deal. While military experts I spoke with were skeptical that the system would be the cure-all for the Ukrainians' need to gain cover and air superiority over Russia — which has been pummeling it with cruise missiles and drones daily, wiping out critical infrastructure including heat and electricity — it may send a distinct signal of escalation to Putin. Whether that is deliberate or not, the Russians have already responded, with the Kremlin's spokesperson reportedly saying the Patriot will be considered a legitimate target.
Until now, the administration has been hesitant to send long range missile systems to Ukraine and for good reason, say experts, who note that the training on the Patriot takes about six months. In the U.S. Army, a "line battery" of upwards of 90 soldiers are required for the ongoing control and command of the system, which gives you an idea of how complex it is. The cost for each system is around $1 billion, not including the missiles. When the United States sent a system, with missiles, to Bahrain in 2019, it cost the Gulf country $2.5 billion. According to this report, Poland's first procurement of the Patriot missile system was $4.75 billion. Mark Cancian, former military officer, now an analyst at CSIS, says that sending it to Ukraine is a big decision for the administration:
“This is going to be the most challenging piece of equipment that Ukraine has received to date... . If the Ukrainians had a year or two to absorb the Patriot, that would not be a problem. … My guess is that the Pentagon is very nervous about this.”
Cancian said the Pentagon is “taking quite a risk here” in deploying the Patriot system. “I think they decided that because the need for air defense was so great, that they were willing to take a risk that was not the case in the past.”
Questions abound. Have Ukrainians already been trained on Patriot missiles, like in Germany? The Washington Post reports that training has not taken place yet and the "parameters" of such a training are being worked out and will "likely" take place in Germany. So when will the system be sent?
From my colleague George Beebe, director of Grand Strategy for the Quincy Institute:
Ukraine has been asking for Patriots for many months, but the U.S. had been reluctant to supply them largely because it had concerns that the Ukrainians could not operate them effectively. Washington has grown more confident the Ukrainians can handle the Patriot, and they help to relieve political pressure in the West to do something to defend against Russia's large-scale strikes on Ukrainian infrastructure. Although the Patriot may help on the margins against these strikes, it is a very expensive and not very efficient means of defending against drone attacks.
Some experts say that while Patriot systems are "the gold standard" of air defense, they can only protect upwards of 68 kilometers of area, so multiple systems would be ideal to provide the overall protection that Ukraine is looking for.
"The Patriot is a point defense system which means that a single battery can defend an area of a few blocks rather than an entire city. The battery also needs to be oriented in the proper direction since its radar system is static. It works well when the target approaches within the search range, but will miss anything that isn't. To establish an effective all-around defense of a particular area, you would need multiple Patriot systems to provide the coverage necessary to watch all avenues of approach," one military expert tells me on background.
In addition, NASAMs which the U.S. already provides, are better for countering drones and cruise missiles, according to retired Army Col. Doug Macgregor. That is what the Russians are using now to attack Ukrainian infrastructure.
However, if the Russians start getting ballistic missiles from Iran and using them — which has not happened yet — Patriot missiles would be better to counter them.
The Defense Department told the Washington Post that the administration will not sign off on the plan until "the Pentagon has answered all questions about training and maintenance, the legalities of a transfer, and its effect on U.S. military readiness." But an announcement is expected as early as Thursday.
UPDATE 12/15 4p.m. ET:
According to the Associated Press Thursday, Russia’s Foreign Ministry spokesperson Maria Zakharova said in a weekly briefing that if Washington follows through with reported plans to send the Patriot Missile system to Ukraine that it would be “another provocative move by the U.S.” that could prompt a response from Moscow, and that the U.S. had “effectively become a party” to the war in Ukraine.